Introduction
In the rapidly evolving landscape of AI-powered applications, effective management of OpenAI API keys has become crucial for developers and organizations. Whether you're building chatbots, content generators, or complex AI systems, understanding how to properly implement, monitor, and optimize your API key usage can make the difference between a successful, cost-effective deployment and an expensive, inefficient one.
This comprehensive guide will walk you through everything you need to know about OpenAI API key usage, from basic implementation across multiple programming languages to advanced monitoring strategies and cost optimization techniques. We'll explore practical examples, best practices, and how platforms like LaoZhang.ai can simplify and enhance your API management experience.
Multi-Language Implementation Guide
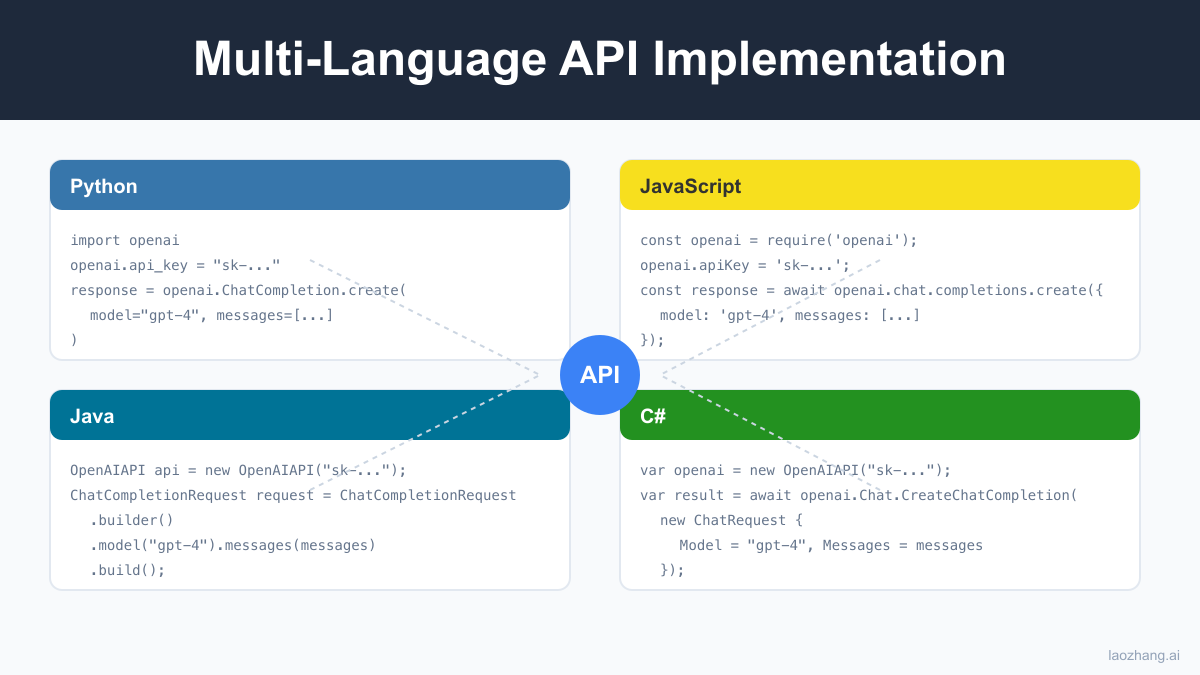
Python Implementation
Python remains one of the most popular languages for AI development. Here's how to properly implement OpenAI API key usage in Python:
pythonimport os from openai import OpenAI from datetime import datetime import json class OpenAIManager: def __init__(self, api_key=None): # Best practice: Use environment variables self.api_key = api_key or os.environ.get('OPENAI_API_KEY') if not self.api_key: raise ValueError("API key not found") self.client = OpenAI(api_key=self.api_key) self.usage_log = [] def make_request(self, prompt, model="gpt-3.5-turbo", max_tokens=100): """Make a request with usage tracking""" try: response = self.client.chat.completions.create( model=model, messages=[ {"role": "user", "content": prompt} ], max_tokens=max_tokens ) # Log usage usage_data = { "timestamp": datetime.now().isoformat(), "model": model, "prompt_tokens": response.usage.prompt_tokens, "completion_tokens": response.usage.completion_tokens, "total_tokens": response.usage.total_tokens } self.usage_log.append(usage_data) return response.choices[0].message.content except Exception as e: print(f"Error: {str(e)}") return None def get_usage_summary(self): """Get summary of API usage""" total_tokens = sum(log['total_tokens'] for log in self.usage_log) return { "total_requests": len(self.usage_log), "total_tokens": total_tokens, "average_tokens_per_request": total_tokens / len(self.usage_log) if self.usage_log else 0 } # Example usage api_manager = OpenAIManager() response = api_manager.make_request("Explain quantum computing in simple terms") print(f"Usage summary: {api_manager.get_usage_summary()}")
JavaScript/Node.js Implementation
For web developers and Node.js applications, here's a robust implementation:
javascriptconst OpenAI = require('openai'); const fs = require('fs').promises; const path = require('path'); class OpenAIUsageTracker { constructor(apiKey) { this.openai = new OpenAI({ apiKey: apiKey || process.env.OPENAI_API_KEY }); this.usageData = []; this.rateLimiter = new RateLimiter(); } async makeRequest(prompt, options = {}) { // Check rate limits if (!this.rateLimiter.canMakeRequest()) { throw new Error('Rate limit exceeded. Please wait.'); } const defaultOptions = { model: 'gpt-3.5-turbo', max_tokens: 100, temperature: 0.7 }; const requestOptions = { ...defaultOptions, ...options }; const startTime = Date.now(); try { const completion = await this.openai.chat.completions.create({ model: requestOptions.model, messages: [{ role: 'user', content: prompt }], max_tokens: requestOptions.max_tokens, temperature: requestOptions.temperature }); // Track usage const usage = { timestamp: new Date().toISOString(), model: requestOptions.model, promptTokens: completion.usage.prompt_tokens, completionTokens: completion.usage.completion_tokens, totalTokens: completion.usage.total_tokens, responseTime: Date.now() - startTime, cost: this.calculateCost(completion.usage, requestOptions.model) }; this.usageData.push(usage); await this.saveUsageData(usage); return completion.choices[0].message.content; } catch (error) { console.error('API request failed:', error); throw error; } } calculateCost(usage, model) { // Cost per 1K tokens (example rates) const rates = { 'gpt-3.5-turbo': { prompt: 0.0015, completion: 0.002 }, 'gpt-4': { prompt: 0.03, completion: 0.06 } }; const modelRates = rates[model] || rates['gpt-3.5-turbo']; const promptCost = (usage.prompt_tokens / 1000) * modelRates.prompt; const completionCost = (usage.completion_tokens / 1000) * modelRates.completion; return { prompt: promptCost, completion: completionCost, total: promptCost + completionCost }; } async saveUsageData(usage) { const logPath = path.join(__dirname, 'usage_logs', `${new Date().toISOString().split('T')[0]}.json`); try { let existingData = []; try { const fileContent = await fs.readFile(logPath, 'utf8'); existingData = JSON.parse(fileContent); } catch (error) { // File doesn't exist yet } existingData.push(usage); await fs.writeFile(logPath, JSON.stringify(existingData, null, 2)); } catch (error) { console.error('Failed to save usage data:', error); } } getUsageAnalytics() { const totalTokens = this.usageData.reduce((sum, usage) => sum + usage.totalTokens, 0); const totalCost = this.usageData.reduce((sum, usage) => sum + usage.cost.total, 0); const avgResponseTime = this.usageData.reduce((sum, usage) => sum + usage.responseTime, 0) / this.usageData.length; return { totalRequests: this.usageData.length, totalTokens, totalCost: totalCost.toFixed(4), averageResponseTime: avgResponseTime.toFixed(2), tokenDistribution: { prompt: this.usageData.reduce((sum, usage) => sum + usage.promptTokens, 0), completion: this.usageData.reduce((sum, usage) => sum + usage.completionTokens, 0) } }; } } class RateLimiter { constructor(maxRequests = 60, windowMs = 60000) { this.maxRequests = maxRequests; this.windowMs = windowMs; this.requests = []; } canMakeRequest() { const now = Date.now(); this.requests = this.requests.filter(timestamp => now - timestamp < this.windowMs); if (this.requests.length < this.maxRequests) { this.requests.push(now); return true; } return false; } getWaitTime() { if (this.requests.length < this.maxRequests) return 0; const oldestRequest = Math.min(...this.requests); return Math.max(0, this.windowMs - (Date.now() - oldestRequest)); } } // Example usage const tracker = new OpenAIUsageTracker();
Java Implementation
For enterprise applications using Java:
javaimport com.theokanning.openai.OpenAiService; import com.theokanning.openai.completion.chat.*; import java.time.LocalDateTime; import java.util.*; import java.util.concurrent.*; import java.io.*; public class OpenAIUsageManager { private final OpenAiService service; private final List<UsageRecord> usageHistory; private final ExecutorService executor; private final RateLimiter rateLimiter; public OpenAIUsageManager(String apiKey) { this.service = new OpenAiService(apiKey); this.usageHistory = Collections.synchronizedList(new ArrayList<>()); this.executor = Executors.newCachedThreadPool(); this.rateLimiter = new RateLimiter(60, 60000); // 60 requests per minute } public CompletableFuture<ChatResponse> makeAsyncRequest(String prompt, String model, int maxTokens) { return CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> { try { // Rate limiting rateLimiter.acquire(); List<ChatMessage> messages = Arrays.asList( new ChatMessage(ChatMessageRole.USER.value(), prompt) ); ChatCompletionRequest request = ChatCompletionRequest.builder() .model(model) .messages(messages) .maxTokens(maxTokens) .temperature(0.7) .build(); long startTime = System.currentTimeMillis(); ChatCompletionResult result = service.createChatCompletion(request); long endTime = System.currentTimeMillis(); // Track usage UsageRecord record = new UsageRecord( LocalDateTime.now(), model, result.getUsage().getPromptTokens(), result.getUsage().getCompletionTokens(), result.getUsage().getTotalTokens(), endTime - startTime, calculateCost(result.getUsage(), model) ); usageHistory.add(record); persistUsageRecord(record); return new ChatResponse( result.getChoices().get(0).getMessage().getContent(), record ); } catch (Exception e) { throw new RuntimeException("API request failed", e); } }, executor); } private double calculateCost(Usage usage, String model) { Map<String, Double[]> rates = new HashMap<>(); rates.put("gpt-3.5-turbo", new Double[]{0.0015, 0.002}); // prompt, completion per 1K tokens rates.put("gpt-4", new Double[]{0.03, 0.06}); Double[] modelRates = rates.getOrDefault(model, rates.get("gpt-3.5-turbo")); double promptCost = (usage.getPromptTokens() / 1000.0) * modelRates[0]; double completionCost = (usage.getCompletionTokens() / 1000.0) * modelRates[1]; return promptCost + completionCost; } private void persistUsageRecord(UsageRecord record) { try { String filename = String.format("usage_%s.csv", LocalDateTime.now().toLocalDate().toString()); try (PrintWriter writer = new PrintWriter(new FileWriter(filename, true))) { writer.println(record.toCsv()); } } catch (IOException e) { System.err.println("Failed to persist usage record: " + e.getMessage()); } } public UsageAnalytics getAnalytics() { synchronized (usageHistory) { if (usageHistory.isEmpty()) { return new UsageAnalytics(); } long totalTokens = usageHistory.stream() .mapToLong(UsageRecord::getTotalTokens) .sum(); double totalCost = usageHistory.stream() .mapToDouble(UsageRecord::getCost) .sum(); double avgResponseTime = usageHistory.stream() .mapToLong(UsageRecord::getResponseTime) .average() .orElse(0); Map<String, Long> modelDistribution = usageHistory.stream() .collect(Collectors.groupingBy( UsageRecord::getModel, Collectors.counting() )); return new UsageAnalytics( usageHistory.size(), totalTokens, totalCost, avgResponseTime, modelDistribution ); } } // Inner classes static class UsageRecord { private final LocalDateTime timestamp; private final String model; private final long promptTokens; private final long completionTokens; private final long totalTokens; private final long responseTime; private final double cost; // Constructor and getters... public String toCsv() { return String.format("%s,%s,%d,%d,%d,%d,%.4f", timestamp, model, promptTokens, completionTokens, totalTokens, responseTime, cost); } } static class RateLimiter { private final int maxRequests; private final long windowMs; private final Semaphore semaphore; private final Queue<Long> requestTimes; public RateLimiter(int maxRequests, long windowMs) { this.maxRequests = maxRequests; this.windowMs = windowMs; this.semaphore = new Semaphore(maxRequests); this.requestTimes = new ConcurrentLinkedQueue<>(); } public void acquire() throws InterruptedException { cleanOldRequests(); semaphore.acquire(); requestTimes.offer(System.currentTimeMillis()); } private void cleanOldRequests() { long cutoff = System.currentTimeMillis() - windowMs; while (!requestTimes.isEmpty() && requestTimes.peek() < cutoff) { requestTimes.poll(); semaphore.release(); } } } }
Usage Monitoring and Analytics
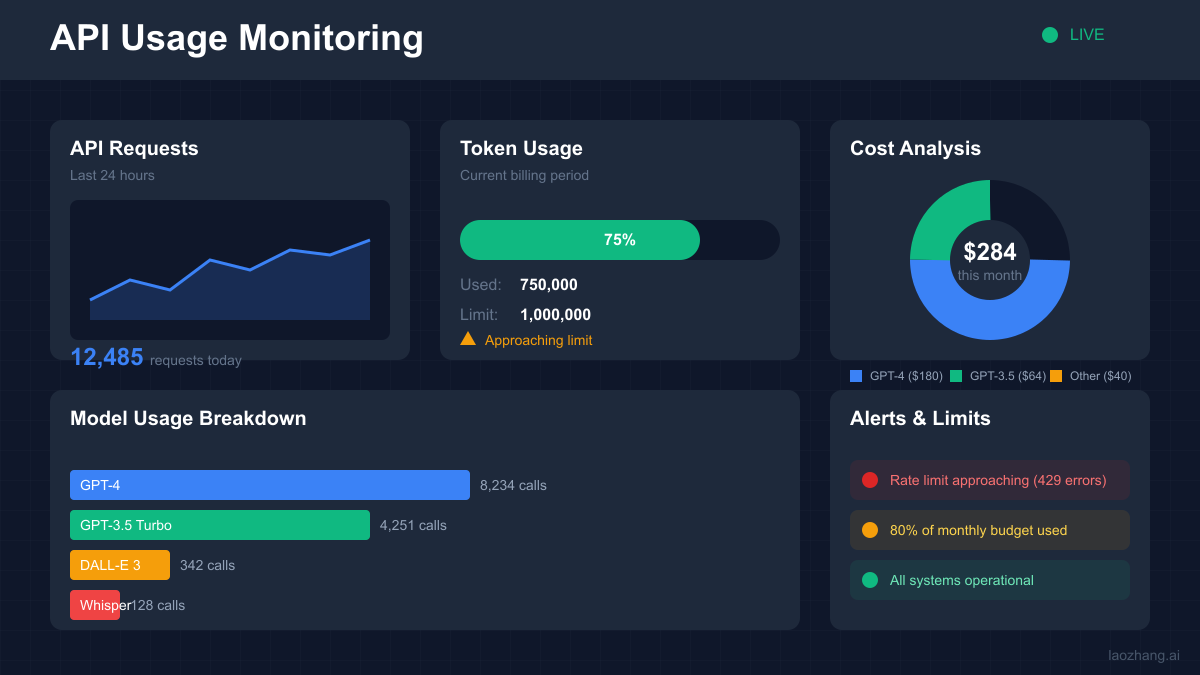
Effective monitoring of your OpenAI API usage is crucial for maintaining control over costs and performance. Here's a comprehensive monitoring system:
pythonimport pandas as pd import matplotlib.pyplot as plt from datetime import datetime, timedelta import json from collections import defaultdict class OpenAIUsageMonitor: def __init__(self, log_file='usage_logs.json'): self.log_file = log_file self.usage_data = self.load_usage_data() def load_usage_data(self): try: with open(self.log_file, 'r') as f: return json.load(f) except FileNotFoundError: return [] def add_usage_record(self, record): """Add a new usage record""" self.usage_data.append(record) self.save_usage_data() def save_usage_data(self): """Persist usage data to file""" with open(self.log_file, 'w') as f: json.dump(self.usage_data, f, indent=2) def get_usage_by_period(self, start_date, end_date): """Get usage statistics for a specific period""" filtered_data = [ record for record in self.usage_data if start_date <= datetime.fromisoformat(record['timestamp']) <= end_date ] if not filtered_data: return None total_tokens = sum(record['total_tokens'] for record in filtered_data) total_cost = sum(record['cost']['total'] for record in filtered_data) return { 'period': f"{start_date.date()} to {end_date.date()}", 'total_requests': len(filtered_data), 'total_tokens': total_tokens, 'total_cost': total_cost, 'average_tokens_per_request': total_tokens / len(filtered_data), 'average_cost_per_request': total_cost / len(filtered_data), 'model_distribution': self._get_model_distribution(filtered_data) } def _get_model_distribution(self, data): """Get distribution of usage by model""" model_usage = defaultdict(lambda: {'count': 0, 'tokens': 0, 'cost': 0}) for record in data: model = record['model'] model_usage[model]['count'] += 1 model_usage[model]['tokens'] += record['total_tokens'] model_usage[model]['cost'] += record['cost']['total'] return dict(model_usage) def generate_usage_report(self, days=30): """Generate a comprehensive usage report""" end_date = datetime.now() start_date = end_date - timedelta(days=days) # Daily usage daily_usage = defaultdict(lambda: {'requests': 0, 'tokens': 0, 'cost': 0}) for record in self.usage_data: timestamp = datetime.fromisoformat(record['timestamp']) if start_date <= timestamp <= end_date: date_key = timestamp.date().isoformat() daily_usage[date_key]['requests'] += 1 daily_usage[date_key]['tokens'] += record['total_tokens'] daily_usage[date_key]['cost'] += record['cost']['total'] # Create visualizations self._create_usage_charts(daily_usage) # Generate summary period_stats = self.get_usage_by_period(start_date, end_date) report = { 'report_date': datetime.now().isoformat(), 'period': f"{days} days", 'summary': period_stats, 'daily_breakdown': dict(daily_usage), 'peak_usage_day': max(daily_usage.items(), key=lambda x: x[1]['tokens'])[0] if daily_usage else None, 'cost_projection': self._project_monthly_cost(period_stats, days) if period_stats else None } return report def _create_usage_charts(self, daily_usage): """Create usage visualization charts""" if not daily_usage: return # Prepare data dates = list(daily_usage.keys()) tokens = [daily_usage[date]['tokens'] for date in dates] costs = [daily_usage[date]['cost'] for date in dates] # Create subplots fig, (ax1, ax2) = plt.subplots(2, 1, figsize=(12, 8)) # Token usage chart ax1.plot(dates, tokens, marker='o', linestyle='-', color='blue') ax1.set_title('Daily Token Usage') ax1.set_xlabel('Date') ax1.set_ylabel('Tokens') ax1.grid(True, alpha=0.3) ax1.tick_params(axis='x', rotation=45) # Cost chart ax2.bar(dates, costs, color='green', alpha=0.7) ax2.set_title('Daily API Costs') ax2.set_xlabel('Date') ax2.set_ylabel('Cost ($)') ax2.grid(True, alpha=0.3) ax2.tick_params(axis='x', rotation=45) plt.tight_layout() plt.savefig('usage_report.png', dpi=300, bbox_inches='tight') plt.close() def _project_monthly_cost(self, period_stats, days): """Project monthly costs based on current usage""" if not period_stats or days == 0: return None daily_average_cost = period_stats['total_cost'] / days return { 'estimated_monthly_cost': daily_average_cost * 30, 'estimated_yearly_cost': daily_average_cost * 365, 'confidence': 'high' if days >= 7 else 'low' } def detect_anomalies(self, threshold_multiplier=2): """Detect unusual usage patterns""" if len(self.usage_data) < 10: return [] # Calculate statistics token_counts = [record['total_tokens'] for record in self.usage_data] mean_tokens = sum(token_counts) / len(token_counts) std_tokens = (sum((x - mean_tokens) <strong> 2 for x in token_counts) / len(token_counts)) </strong> 0.5 anomalies = [] threshold = mean_tokens + (threshold_multiplier * std_tokens) for record in self.usage_data: if record['total_tokens'] > threshold: anomalies.append({ 'timestamp': record['timestamp'], 'tokens': record['total_tokens'], 'deviation': (record['total_tokens'] - mean_tokens) / std_tokens, 'cost': record['cost']['total'] }) return anomalies # Real-time monitoring dashboard class RealTimeMonitor: def __init__(self): self.current_minute_requests = 0 self.current_hour_requests = 0 self.current_day_tokens = 0 self.alerts = [] def track_request(self, tokens, cost): """Track a new request in real-time""" self.current_minute_requests += 1 self.current_hour_requests += 1 self.current_day_tokens += tokens # Check thresholds self.check_thresholds(tokens, cost) def check_thresholds(self, tokens, cost): """Check if any thresholds are exceeded""" # Configurable thresholds thresholds = { 'minute_requests': 50, 'hour_requests': 500, 'day_tokens': 1000000, 'single_request_cost': 1.0 } if self.current_minute_requests > thresholds['minute_requests']: self.alerts.append({ 'type': 'rate_limit_warning', 'message': f'High request rate: {self.current_minute_requests} requests/minute', 'timestamp': datetime.now().isoformat() }) if cost > thresholds['single_request_cost']: self.alerts.append({ 'type': 'cost_warning', 'message': f'Expensive request: ${cost:.2f}', 'timestamp': datetime.now().isoformat() })
Rate Limits and Tier Management
Understanding and managing rate limits is crucial for maintaining reliable API access:
pythonclass RateLimitManager: # OpenAI rate limits by tier (as of 2024) TIER_LIMITS = { 'free': { 'rpm': 3, # requests per minute 'rpd': 200, # requests per day 'tpm': 40000, # tokens per minute 'tpd': 1000000 # tokens per day }, 'tier_1': { 'rpm': 60, 'tpm': 60000, 'rpd': 10000, 'tpd': 10000000 }, 'tier_2': { 'rpm': 500, 'tpm': 80000, 'rpd': 50000, 'tpd': 50000000 }, 'tier_3': { 'rpm': 5000, 'tpm': 160000, 'rpd': 100000, 'tpd': 100000000 }, 'tier_4': { 'rpm': 10000, 'tpm': 1000000, 'rpd': 1000000, 'tpd': 1000000000 } } def __init__(self, tier='tier_1'): self.tier = tier self.limits = self.TIER_LIMITS[tier] self.request_history = deque() self.token_history = deque() self.daily_requests = 0 self.daily_tokens = 0 self.last_reset = datetime.now() def can_make_request(self, estimated_tokens): """Check if a request can be made within rate limits""" current_time = datetime.now() # Reset daily counters if needed if (current_time - self.last_reset).days >= 1: self.daily_requests = 0 self.daily_tokens = 0 self.last_reset = current_time # Clean old entries minute_ago = current_time - timedelta(minutes=1) self.request_history = deque( t for t in self.request_history if t > minute_ago ) self.token_history = deque( (t, tokens) for t, tokens in self.token_history if t > minute_ago ) # Check all limits minute_requests = len(self.request_history) minute_tokens = sum(tokens for _, tokens in self.token_history) checks = { 'rpm': minute_requests < self.limits['rpm'], 'tpm': minute_tokens + estimated_tokens <= self.limits['tpm'], 'rpd': self.daily_requests < self.limits['rpd'], 'tpd': self.daily_tokens + estimated_tokens <= self.limits['tpd'] } return all(checks.values()), checks def record_request(self, tokens_used): """Record a completed request""" current_time = datetime.now() self.request_history.append(current_time) self.token_history.append((current_time, tokens_used)) self.daily_requests += 1 self.daily_tokens += tokens_used def get_wait_time(self): """Calculate how long to wait before next request""" if not self.request_history: return 0 oldest_request = self.request_history[0] time_since_oldest = (datetime.now() - oldest_request).total_seconds() if time_since_oldest < 60: return 60 - time_since_oldest return 0 def upgrade_tier_recommendation(self): """Recommend tier upgrade based on usage patterns""" if self.daily_requests > self.limits['rpd'] * 0.8: for tier_name, tier_limits in self.TIER_LIMITS.items(): if tier_limits['rpd'] > self.limits['rpd']: return { 'recommended_tier': tier_name, 'reason': 'Approaching daily request limit', 'current_usage': f"{self.daily_requests}/{self.limits['rpd']} requests" } return None
Best Practices for Efficient Usage
1. Token Optimization
pythonclass TokenOptimizer: def __init__(self): self.encoding = tiktoken.encoding_for_model("gpt-3.5-turbo") def optimize_prompt(self, prompt, max_tokens=2000): """Optimize prompt to use fewer tokens""" # Remove unnecessary whitespace prompt = ' '.join(prompt.split()) # Count tokens token_count = len(self.encoding.encode(prompt)) if token_count <= max_tokens: return prompt, token_count # Truncate if necessary tokens = self.encoding.encode(prompt) truncated_tokens = tokens[:max_tokens] optimized_prompt = self.encoding.decode(truncated_tokens) return optimized_prompt, max_tokens def batch_prompts(self, prompts, max_batch_tokens=4000): """Batch multiple prompts efficiently""" batches = [] current_batch = [] current_tokens = 0 for prompt in prompts: tokens = len(self.encoding.encode(prompt)) if current_tokens + tokens > max_batch_tokens: if current_batch: batches.append(current_batch) current_batch = [prompt] current_tokens = tokens else: current_batch.append(prompt) current_tokens += tokens if current_batch: batches.append(current_batch) return batches
2. Caching Strategy
pythonimport hashlib import redis from functools import wraps class APICache: def __init__(self, redis_client=None, ttl=3600): self.cache = redis_client or {} # Use dict if Redis not available self.ttl = ttl def cache_key(self, prompt, model, params): """Generate cache key from request parameters""" key_data = f"{prompt}:{model}:{json.dumps(params, sort_keys=True)}" return hashlib.md5(key_data.encode()).hexdigest() def cached_request(self, func): """Decorator for caching API responses""" @wraps(func) def wrapper(prompt, model='gpt-3.5-turbo', **kwargs): cache_key = self.cache_key(prompt, model, kwargs) # Check cache if isinstance(self.cache, dict): cached = self.cache.get(cache_key) else: cached = self.cache.get(cache_key) if cached: cached = json.loads(cached) if cached: return cached['response'], cached['usage'] # Make API call response, usage = func(prompt, model, **kwargs) # Cache result cache_data = { 'response': response, 'usage': usage, 'timestamp': datetime.now().isoformat() } if isinstance(self.cache, dict): self.cache[cache_key] = cache_data else: self.cache.setex( cache_key, self.ttl, json.dumps(cache_data) ) return response, usage return wrapper
3. Error Handling and Recovery
pythonclass RobustAPIClient: def __init__(self, api_key, max_retries=3): self.client = OpenAI(api_key=api_key) self.max_retries = max_retries def make_request_with_fallback(self, prompt, models=['gpt-3.5-turbo', 'gpt-3.5-turbo-16k']): """Make request with model fallback""" errors = [] for model in models: try: return self._make_request_with_retry(prompt, model) except Exception as e: errors.append(f"{model}: {str(e)}") continue raise Exception(f"All models failed: {'; '.join(errors)}") def _make_request_with_retry(self, prompt, model): """Make request with exponential backoff retry""" for attempt in range(self.max_retries): try: response = self.client.chat.completions.create( model=model, messages=[{"role": "user", "content": prompt}], timeout=30 ) return response except RateLimitError as e: wait_time = 2 ** attempt * 5 # Exponential backoff print(f"Rate limit hit. Waiting {wait_time}s...") time.sleep(wait_time) except APIConnectionError as e: if attempt == self.max_retries - 1: raise time.sleep(2 ** attempt) except Exception as e: if attempt == self.max_retries - 1: raise time.sleep(1)
Cost Tracking and Optimization
Effective cost management is essential for sustainable API usage:
pythonclass CostOptimizer: def __init__(self, budget_limit=100.0): self.budget_limit = budget_limit self.current_spend = 0.0 self.cost_history = [] def track_cost(self, tokens, model, usage_type='completion'): """Track costs for each API call""" cost = self.calculate_cost(tokens, model, usage_type) self.current_spend += cost record = { 'timestamp': datetime.now().isoformat(), 'tokens': tokens, 'model': model, 'cost': cost, 'cumulative_spend': self.current_spend } self.cost_history.append(record) # Check budget if self.current_spend > self.budget_limit: self._trigger_budget_alert() return cost def calculate_cost(self, tokens, model, usage_type): """Calculate cost based on current pricing""" pricing = { 'gpt-3.5-turbo': { 'prompt': 0.0015 / 1000, 'completion': 0.002 / 1000 }, 'gpt-4': { 'prompt': 0.03 / 1000, 'completion': 0.06 / 1000 }, 'gpt-4-turbo': { 'prompt': 0.01 / 1000, 'completion': 0.03 / 1000 } } model_pricing = pricing.get(model, pricing['gpt-3.5-turbo']) rate = model_pricing.get(usage_type, model_pricing['completion']) return tokens * rate def get_cost_breakdown(self, period_days=30): """Get detailed cost breakdown""" cutoff_date = datetime.now() - timedelta(days=period_days) period_costs = [ record for record in self.cost_history if datetime.fromisoformat(record['timestamp']) > cutoff_date ] # Group by model model_costs = defaultdict(float) daily_costs = defaultdict(float) for record in period_costs: model_costs[record['model']] += record['cost'] date_key = record['timestamp'].split('T')[0] daily_costs[date_key] += record['cost'] return { 'total_cost': sum(model_costs.values()), 'model_breakdown': dict(model_costs), 'daily_average': sum(daily_costs.values()) / len(daily_costs) if daily_costs else 0, 'projection_monthly': (sum(daily_costs.values()) / period_days) * 30 if period_days > 0 else 0 } def optimize_model_selection(self, prompt, quality_threshold=0.8): """Select most cost-effective model for the task""" # Estimate complexity complexity = self._estimate_prompt_complexity(prompt) if complexity < 0.3: return 'gpt-3.5-turbo' # Simple tasks elif complexity < 0.7: return 'gpt-4-turbo' # Medium complexity else: return 'gpt-4' # Complex tasks def _estimate_prompt_complexity(self, prompt): """Estimate prompt complexity (0-1)""" # Simple heuristic based on length and keywords complexity_indicators = [ 'analyze', 'complex', 'detailed', 'comprehensive', 'technical', 'advanced', 'expert', 'sophisticated' ] base_complexity = min(len(prompt) / 1000, 0.5) keyword_bonus = sum(0.1 for word in complexity_indicators if word in prompt.lower()) return min(base_complexity + keyword_bonus, 1.0)
LaoZhang.ai Integration Benefits
LaoZhang.ai provides significant advantages for OpenAI API usage management:
1. Unified API Management
pythonclass LaoZhangAPIManager: def __init__(self, laozhang_api_key): self.api_key = laozhang_api_key self.base_url = "https://api.laozhang.ai/v1" def make_request(self, prompt, model='gpt-3.5-turbo'): """Make request through LaoZhang.ai proxy""" headers = { 'Authorization': f'Bearer {self.api_key}', 'Content-Type': 'application/json' } data = { 'model': model, 'messages': [{'role': 'user', 'content': prompt}], 'stream': False } response = requests.post( f'{self.base_url}/chat/completions', headers=headers, json=data ) if response.status_code == 200: result = response.json() # LaoZhang.ai provides enhanced usage data usage_data = { 'tokens': result['usage'], 'cost': result.get('cost', {}), 'credits_remaining': result.get('credits_remaining'), 'rate_limit_remaining': result.get('rate_limit_remaining') } return result['choices'][0]['message']['content'], usage_data else: raise Exception(f"API error: {response.status_code}")
2. Built-in Cost Management
LaoZhang.ai offers prepaid credits system with real-time tracking:
pythonclass LaoZhangCostManager: def __init__(self, api_client): self.client = api_client def check_balance(self): """Check current credit balance""" response = self.client.get('/account/balance') return { 'credits': response['credits'], 'usd_equivalent': response['credits'] * 0.01, # 1 credit = \$0.01 'usage_this_month': response['monthly_usage'] } def set_spending_limit(self, daily_limit, monthly_limit): """Set spending limits""" return self.client.post('/account/limits', { 'daily_limit': daily_limit, 'monthly_limit': monthly_limit }) def get_usage_alerts(self): """Get usage alerts and recommendations""" return self.client.get('/account/alerts')
3. Enhanced Monitoring Dashboard
LaoZhang.ai provides a comprehensive dashboard with:
- Real-time usage statistics
- Cost breakdowns by model and time period
- API performance metrics
- Automated alerts for unusual usage patterns
4. Simplified Multi-Model Access
pythonclass LaoZhangMultiModel: def __init__(self, api_key): self.api_key = api_key self.models = { 'fast': 'gpt-3.5-turbo', 'balanced': 'gpt-4-turbo', 'quality': 'gpt-4', 'claude': 'claude-3-sonnet', 'llama': 'llama-3-70b' } def smart_route(self, prompt, requirements=None): """Intelligently route to appropriate model""" if requirements: if requirements.get('speed') == 'fast': model = self.models['fast'] elif requirements.get('quality') == 'high': model = self.models['quality'] else: model = self.models['balanced'] else: # Auto-select based on prompt analysis model = self._analyze_and_select(prompt) return self.make_request(prompt, model)
Advanced Usage Patterns
1. Streaming Responses with Token Tracking
pythonclass StreamingUsageTracker: def __init__(self, api_client): self.client = api_client self.current_stream_tokens = 0 async def stream_with_tracking(self, prompt, model='gpt-3.5-turbo'): """Stream responses while tracking token usage""" stream = await self.client.chat.completions.create( model=model, messages=[{"role": "user", "content": prompt}], stream=True ) full_response = "" token_count = 0 async for chunk in stream: if chunk.choices[0].delta.content: content = chunk.choices[0].delta.content full_response += content # Estimate tokens (rough approximation) token_count += len(content.split()) * 1.3 yield content, token_count # Record final usage self.record_stream_usage(prompt, full_response, token_count, model)
2. Parallel Request Processing
pythonimport asyncio from concurrent.futures import ThreadPoolExecutor class ParallelAPIProcessor: def __init__(self, api_key, max_workers=5): self.api_key = api_key self.executor = ThreadPoolExecutor(max_workers=max_workers) self.rate_limiter = RateLimiter(max_requests=50) async def process_batch(self, prompts, model='gpt-3.5-turbo'): """Process multiple prompts in parallel""" tasks = [] results = [] for i, prompt in enumerate(prompts): # Rate limiting await self.rate_limiter.acquire() task = asyncio.create_task( self._process_single(prompt, model, i) ) tasks.append(task) # Gather results responses = await asyncio.gather(*tasks, return_exceptions=True) # Process results and handle errors for i, response in enumerate(responses): if isinstance(response, Exception): results.append({ 'index': i, 'error': str(response), 'prompt': prompts[i] }) else: results.append({ 'index': i, 'response': response['content'], 'usage': response['usage'] }) return results
3. Conversation Context Management
pythonclass ConversationManager: def __init__(self, max_context_tokens=4000): self.max_context_tokens = max_context_tokens self.conversations = {} def create_conversation(self, conversation_id): """Create a new conversation""" self.conversations[conversation_id] = { 'messages': [], 'total_tokens': 0, 'created_at': datetime.now() } def add_message(self, conversation_id, role, content): """Add message to conversation with token management""" if conversation_id not in self.conversations: self.create_conversation(conversation_id) conversation = self.conversations[conversation_id] # Estimate tokens message_tokens = self._estimate_tokens(content) # Trim context if necessary while conversation['total_tokens'] + message_tokens > self.max_context_tokens: if len(conversation['messages']) <= 2: # Keep at least system and one user message break # Remove oldest messages removed_message = conversation['messages'].pop(1) # Keep system message conversation['total_tokens'] -= self._estimate_tokens(removed_message['content']) # Add new message conversation['messages'].append({ 'role': role, 'content': content }) conversation['total_tokens'] += message_tokens return conversation['messages'] def get_conversation_context(self, conversation_id): """Get optimized conversation context""" if conversation_id not in self.conversations: return [] return self.conversations[conversation_id]['messages']
Future Considerations
As the AI landscape evolves, consider these future-proofing strategies:
1. Model Version Management
pythonclass ModelVersionManager: def __init__(self): self.model_registry = { 'gpt-3.5-turbo': { 'current': 'gpt-3.5-turbo-0125', 'fallback': 'gpt-3.5-turbo-1106', 'deprecated': ['gpt-3.5-turbo-0613'] }, 'gpt-4': { 'current': 'gpt-4-0125-preview', 'fallback': 'gpt-4-1106-preview', 'deprecated': ['gpt-4-0613'] } } def get_best_model(self, model_family): """Get the best available model version""" if model_family in self.model_registry: return self.model_registry[model_family]['current'] return model_family def migrate_to_new_version(self, old_model, new_model): """Migrate from old to new model version""" migration_plan = { 'old_model': old_model, 'new_model': new_model, 'changes': self._analyze_model_differences(old_model, new_model), 'testing_required': True, 'rollback_plan': self.model_registry.get(old_model, {}).get('fallback') } return migration_plan
2. Multi-Provider Strategy
pythonclass MultiProviderManager: def __init__(self): self.providers = { 'openai': OpenAIClient(), 'anthropic': AnthropicClient(), 'laozhang': LaoZhangClient() } self.provider_health = {} def select_provider(self, requirements): """Select best provider based on requirements""" for provider_name, client in self.providers.items(): if self._check_provider_health(provider_name): if self._meets_requirements(provider_name, requirements): return provider_name, client raise Exception("No suitable provider available") def _check_provider_health(self, provider_name): """Check if provider is healthy""" # Implementation would include health checks return self.provider_health.get(provider_name, True)
Conclusion
Effective OpenAI API key usage management is crucial for building scalable, cost-effective AI applications. By implementing proper monitoring, rate limit management, and optimization strategies, you can ensure your applications run efficiently while maintaining control over costs.
Key takeaways:
- Implement comprehensive usage tracking from the start
- Use rate limiting and caching to optimize API calls
- Monitor costs continuously and set appropriate budgets
- Consider platforms like LaoZhang.ai for simplified management
- Plan for future changes in models and pricing
Whether you're building a simple chatbot or a complex AI system, the patterns and practices outlined in this guide will help you make the most of your OpenAI API usage while avoiding common pitfalls. Remember that API usage optimization is an ongoing process—regularly review your usage patterns and adjust your strategies accordingly.
For developers seeking a streamlined experience with built-in monitoring, cost management, and multi-model support, LaoZhang.ai provides an excellent platform that addresses many of the challenges discussed in this guide. By combining the power of OpenAI's models with intelligent usage management, you can focus on building great applications rather than worrying about API complexities.
