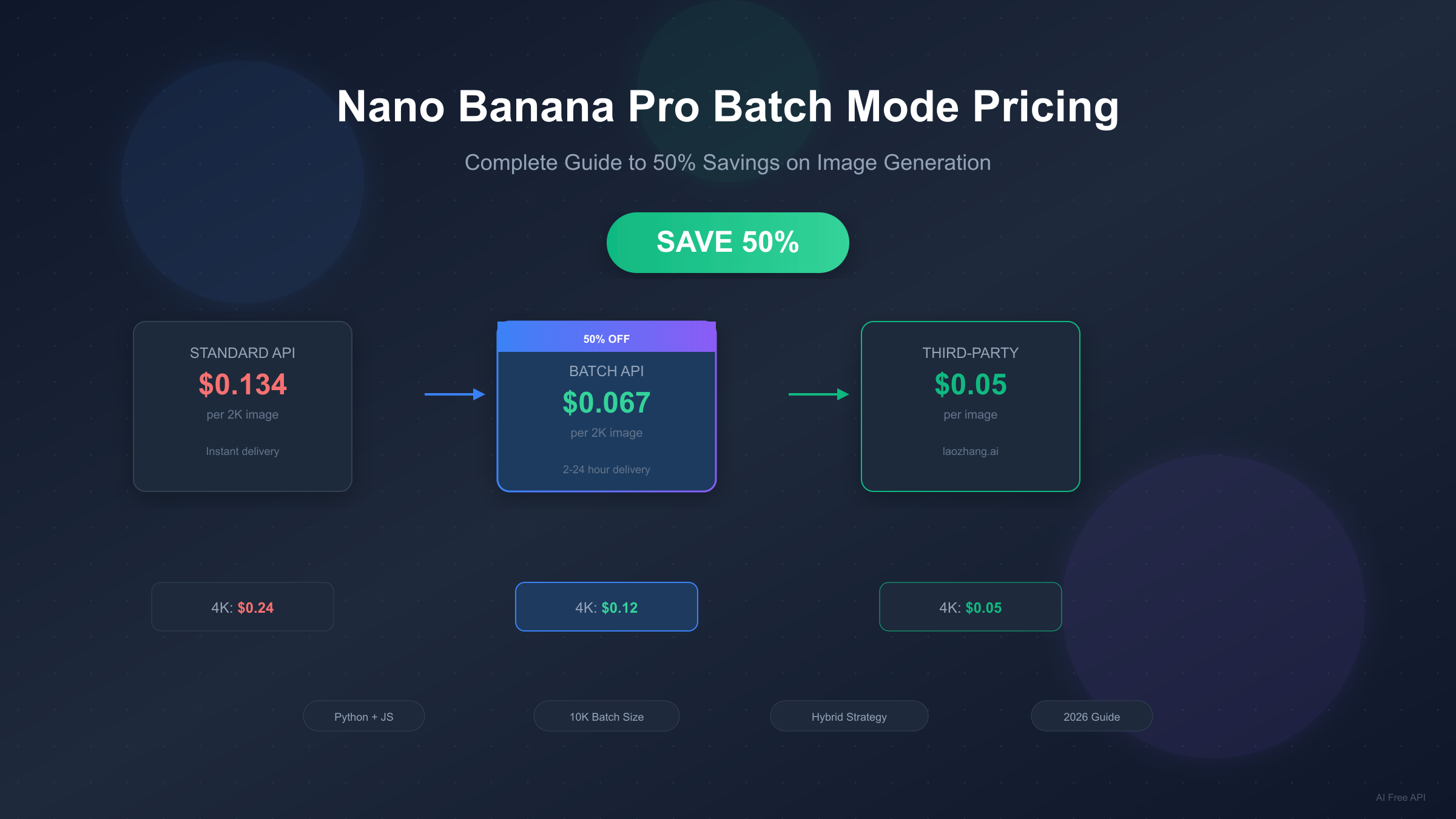
Google's Nano Banana Pro (Gemini 3 Pro Image) delivers stunning 4K images with 94% accuracy and exceptional text rendering. But at $0.134-$0.24 per image, costs can quickly escalate for production workloads. The Batch API changes this equation entirely, offering a flat 50% discount for users who can tolerate asynchronous processing. This guide provides everything you need to implement batch processing effectively—from code examples to hybrid strategies that can reduce your costs by up to 63%.
What is Batch Mode? Understanding the 50% Discount
The Batch API represents Google's most significant cost optimization for high-volume image generation. Rather than processing requests synchronously with immediate responses, batch mode queues your requests for asynchronous processing during Google's lower-demand periods. In exchange for this flexibility, you receive a guaranteed 50% reduction on all generation costs.
Processing times range from 2 to 24 hours, though most jobs complete within 2-6 hours. Google's target SLA is 24 hours, but their infrastructure typically delivers results much faster. The variance depends on system load, batch size, and time of submission. Jobs submitted during off-peak hours (evenings and weekends in US time zones) tend to complete faster.
The batch system accepts up to 10,000 requests per job. You can submit requests either inline (directly in the API call for batches under 20MB) or via JSONL file upload for larger workloads. Each request in a batch processes independently, meaning partial failures don't affect other requests in the same batch.
Quality remains identical to the standard API. The only difference is delivery timing—the same models, same resolutions, same capabilities. You're not sacrificing image quality for cost savings. This makes batch processing ideal for any workflow where immediate delivery isn't essential.
The fundamental tradeoff is simple: instant results at full price, or patience rewarded with 50% savings. For many production use cases—marketing asset libraries, product catalog generation, content pipelines with planning buffers—this tradeoff heavily favors batch processing.
Complete Batch Pricing Breakdown
Understanding the exact numbers helps you calculate potential savings for your specific workload. Nano Banana Pro offers two resolution tiers, each with distinct pricing for standard and batch modes.
| Resolution | Standard API | Batch API | Savings |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1K / 2K | $0.134/image | $0.067/image | 50% ($0.067) |
| 4K | $0.24/image | $0.12/image | 50% ($0.12) |
An important optimization: 1K and 2K share identical pricing. This means choosing 2K over 1K costs nothing extra while providing higher quality output. For any application not specifically requiring minimal file sizes, 2K represents the rational default choice.
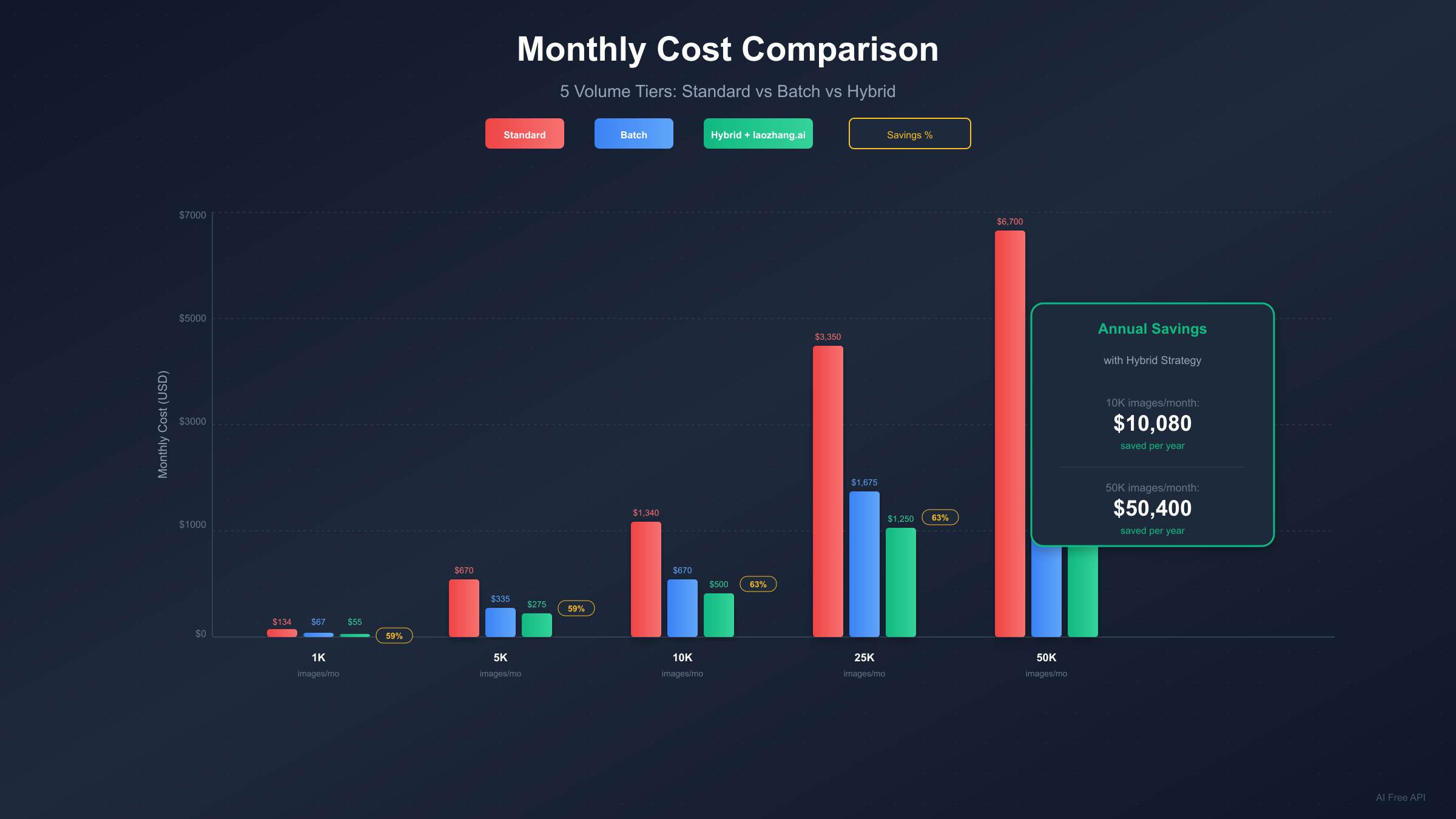
At scale, these savings compound significantly. Consider a marketing team generating 5,000 product images monthly:
| Monthly Volume | Standard Cost | Batch Cost | Monthly Savings | Annual Savings |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1,000 images | $134 | $67 | $67 | $804 |
| 5,000 images | $670 | $335 | $335 | $4,020 |
| 10,000 images | $1,340 | $670 | $670 | $8,040 |
| 25,000 images | $3,350 | $1,675 | $1,675 | $20,100 |
| 50,000 images | $6,700 | $3,350 | $3,350 | $40,200 |
These calculations assume 2K resolution. For 4K workloads, absolute savings are even larger (though percentage remains 50%). A team generating 10,000 4K images monthly saves $1,200 per month—$14,400 annually—simply by switching to batch processing.
For comprehensive pricing details including free tier options, see our Nano Banana Pro API Pricing Guide.
When to Use Batch Mode: The Decision Framework
Not every workload suits batch processing—the key is matching your urgency requirements to the right API tier. This decision matrix helps you identify the optimal approach for different scenarios.
| Urgency Level | Volume | Budget Priority | Recommended Approach |
|---|---|---|---|
| Immediate (<1 min) | Any | Any | Standard API |
| Same-day (1-6 hours) | Low-Medium | Cost-sensitive | Batch API |
| Flexible (6-24 hours) | Any | Cost-optimized | Batch API |
| Overnight/Next-day | High | Maximum savings | Batch API |
| Mixed requirements | High | Balanced | Hybrid Strategy |
Batch mode excels in scheduled content workflows. Marketing teams preparing campaigns days or weeks ahead gain nothing from instant delivery. Product photography pipelines processing catalog updates overnight benefit fully from batch savings. Machine learning teams generating training datasets have no real-time requirements.
Real-time user-facing features require standard API. Interactive applications where users expect immediate results—profile picture generators, live editing tools, chatbot integrations—cannot tolerate batch latency. These workloads justify premium pricing.
The hybrid approach often delivers optimal results. Many production systems combine both modes: batch processing handles 30-60% of volume (scheduled overnight runs, pre-generated assets), while standard API serves real-time user requests. This segmentation maximizes savings without compromising user experience.
Consider your failure recovery requirements. Batch jobs that fail require resubmission and additional waiting. For critical deadline-driven work, building in buffer time accounts for potential retries. Standard API's immediate feedback allows faster iteration when time is constrained.
Hybrid Strategy: Maximizing Cost Efficiency
The most sophisticated cost optimization combines batch processing with third-party providers. Rather than choosing one approach, strategic distribution across multiple tiers delivers maximum savings.
The optimal hybrid distribution typically follows this pattern:
| Tier | Allocation | Use Case | Cost |
|---|---|---|---|
| Third-party (laozhang.ai) | 40-50% | Non-critical, high-volume | $0.05/image |
| Batch API | 30-40% | Scheduled, quality-critical | $0.067-0.12/image |
| Standard API | 10-20% | Real-time, SLA-critical | $0.134-0.24/image |
Third-party providers like laozhang.ai offer compelling economics. At $0.05 per image regardless of resolution, they provide 63% savings versus official standard pricing and 25% savings versus batch pricing. The tradeoff involves routing through intermediary infrastructure, which some enterprise compliance requirements may preclude.
Let's calculate hybrid savings at 10,000 monthly 4K images:
- Pure Standard: 10,000 × $0.24 = $2,400/month
- Pure Batch: 10,000 × $0.12 = $1,200/month
- Hybrid (50% laozhang.ai, 35% Batch, 15% Standard):
- 5,000 × $0.05 = $250
- 3,500 × $0.12 = $420
- 1,500 × $0.24 = $360
- Total: $1,030/month
The hybrid approach saves $1,370 monthly versus standard—$16,440 annually. This represents 57% reduction compared to naive standard API usage.
Implementation requires intelligent request routing. Your application layer must classify requests by urgency and route accordingly. A simple priority queue with three levels handles most scenarios. Overnight batch jobs collect non-urgent requests throughout the day, while real-time requests route directly to standard or third-party endpoints.
For users seeking higher concurrency limits, our Gemini 3 Pro Image Unlimited Concurrency Guide covers scaling strategies.
Implementation Guide with Code Examples
Getting started with batch mode requires minimal code changes from standard API usage. The core difference is submission method and result retrieval pattern.
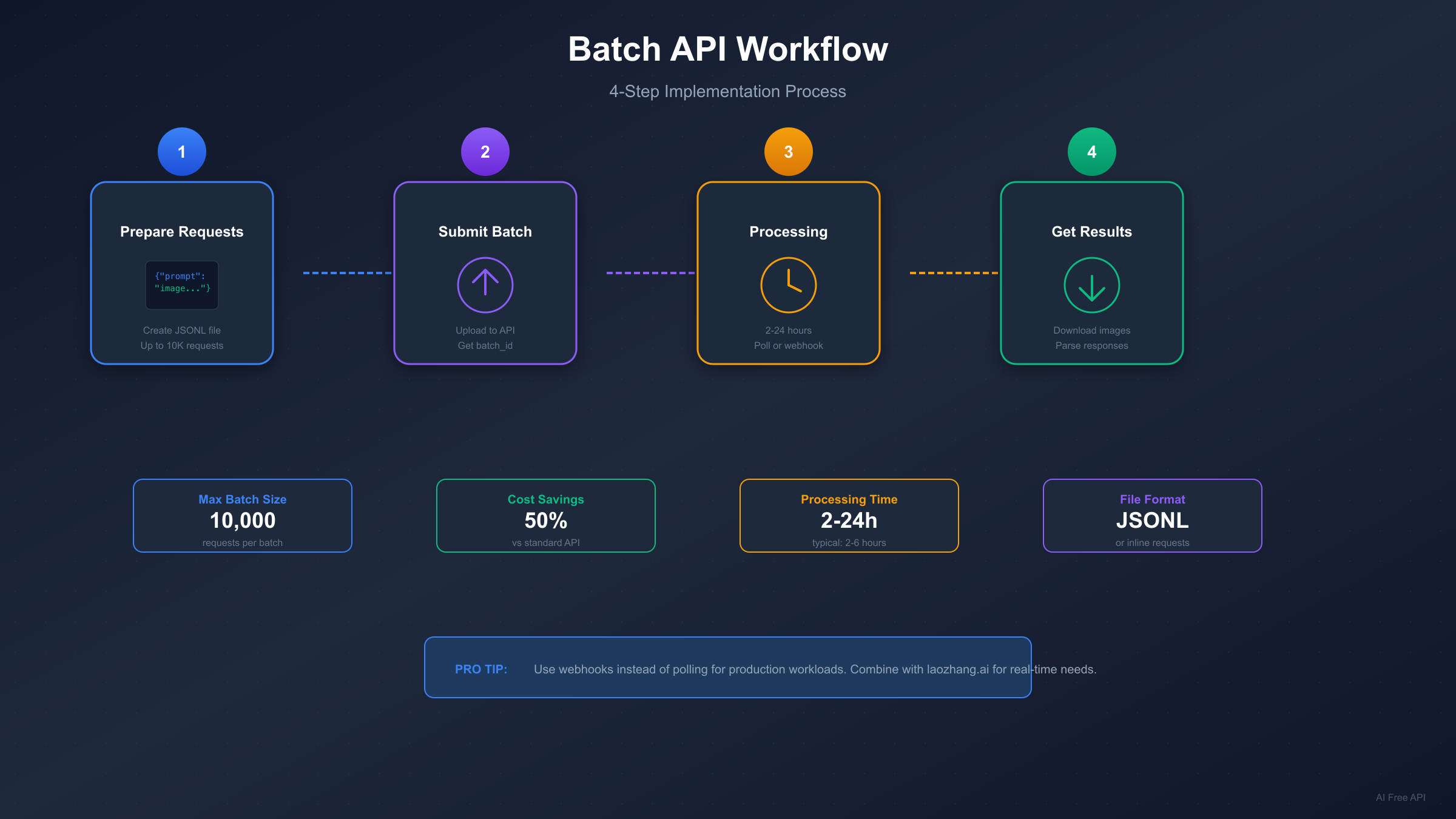
Python Implementation (google-genai SDK):
pythonfrom google import genai import time client = genai.Client(api_key="YOUR_API_KEY") # Prepare batch requests batch_requests = [ { "contents": [{ "parts": [{"text": "A professional product photo of a blue smartphone on white background, 4K quality"}] }], "generationConfig": { "responseModalities": ["TEXT", "IMAGE"] } } for _ in range(100) # 100 images ] # Submit batch job batch_job = client.batches.create( model="models/gemini-2.0-flash-exp", src=batch_requests, config={"display_name": "product-images-batch"} ) print(f"Batch submitted: {batch_job.name}") # Poll for completion while True: job_status = client.batches.get(name=batch_job.name) if job_status.state.name == "JOB_STATE_SUCCEEDED": break elif job_status.state.name == "JOB_STATE_FAILED": raise Exception(f"Batch failed: {job_status.error}") time.sleep(60) # Check every minute # Retrieve results for response in job_status.dest.inlined_responses: # Process each image response image_data = response.candidates[0].content.parts[0].inline_data # Save or process image_data.data (base64 encoded)
JavaScript/Node.js Implementation:
javascriptconst { GoogleGenerativeAI } = require("@google/generative-ai"); const genAI = new GoogleGenerativeAI(process.env.API_KEY); async function submitBatchJob(prompts) { // Prepare JSONL content const jsonlContent = prompts.map((prompt, idx) => JSON.stringify({ key: `request-${idx}`, request: { contents: [{ parts: [{ text: prompt }] }], generationConfig: { responseModalities: ["TEXT", "IMAGE"] } } }) ).join('\n'); // Upload file and create batch const file = await genAI.fileManager.uploadFile( Buffer.from(jsonlContent), { mimeType: "application/jsonl" } ); const batch = await genAI.batchManager.create({ model: "gemini-2.0-flash-exp", srcFile: file.name, displayName: "image-batch-job" }); console.log(`Batch created: ${batch.name}`); return batch.name; } async function pollBatchStatus(batchName) { while (true) { const status = await genAI.batchManager.get(batchName); if (status.state === "SUCCEEDED") { return await genAI.fileManager.download(status.destFile); } else if (status.state === "FAILED") { throw new Error(`Batch failed: ${status.error}`); } await new Promise(r => setTimeout(r, 60000)); // Wait 1 minute } }
For third-party integration, laozhang.ai provides OpenAI-compatible endpoints:
pythonimport openai # laozhang.ai configuration client = openai.OpenAI( api_key="your-laozhang-api-key", base_url="https://api.laozhang.ai/v1" ) response = client.images.generate( model="gemini-3-pro-image", prompt="Professional product photography, white background, 4K", size="1024x1024", n=1 ) image_url = response.data[0].url
For complete free tier options and testing, see our Nano Banana Pro Free Guide.
Production-Ready Error Handling
Robust batch processing requires comprehensive error handling strategies. Unlike synchronous APIs where failures are immediately apparent, batch jobs can fail partially or completely hours after submission.
Implement exponential backoff for transient failures:
pythonimport time import random def submit_with_retry(client, requests, max_retries=5): for attempt in range(max_retries): try: return client.batches.create( model="models/gemini-2.0-flash-exp", src=requests, config={"display_name": f"batch-attempt-{attempt}"} ) except Exception as e: if "RESOURCE_EXHAUSTED" in str(e) or "429" in str(e): wait_time = (2 ** attempt) + random.uniform(0, 1) print(f"Rate limited, waiting {wait_time:.1f}s...") time.sleep(wait_time) else: raise raise Exception("Max retries exceeded")
Handle partial failures within completed batches. Even successful batch jobs may contain failed individual requests. Parse results carefully:
pythondef process_batch_results(batch_job, client): results = {"success": [], "failed": []} for idx, response in enumerate(batch_job.dest.inlined_responses): if hasattr(response, 'error'): results["failed"].append({ "index": idx, "error": response.error.message }) else: results["success"].append({ "index": idx, "image": response.candidates[0].content.parts[0] }) # Optionally resubmit failed requests if results["failed"]: print(f"{len(results['failed'])} requests failed, consider resubmission") return results
Implement idempotency for safe retries. Include unique identifiers in your requests to prevent duplicate processing:
pythonimport uuid def create_idempotent_request(prompt, request_id=None): return { "key": request_id or str(uuid.uuid4()), "request": { "contents": [{"parts": [{"text": prompt}]}], "generationConfig": {"responseModalities": ["TEXT", "IMAGE"]} } }
Set up monitoring for long-running batches. Webhook notifications avoid continuous polling overhead:
python# When creating batch, specify callback URL batch_job = client.batches.create( model="models/gemini-2.0-flash-exp", src=requests, config={ "display_name": "monitored-batch", "notification_config": { "pubsub_topic": "projects/your-project/topics/batch-notifications" } } )
Cost Calculator: 5 Volume Tiers Analyzed
Different volume levels benefit differently from various optimization strategies. This analysis helps you identify the optimal approach for your specific scale.
| Monthly Volume | Standard Only | Batch Only | Hybrid Strategy | Best Savings |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1,000 (2K) | $134 | $67 | $55 | 59% (Hybrid) |
| 5,000 (2K) | $670 | $335 | $275 | 59% (Hybrid) |
| 10,000 (2K) | $1,340 | $670 | $500 | 63% (Hybrid) |
| 25,000 (2K) | $3,350 | $1,675 | $1,250 | 63% (Hybrid) |
| 50,000 (2K) | $6,700 | $3,350 | $2,500 | 63% (Hybrid) |
Hybrid strategy assumptions: 50% via laozhang.ai ($0.05), 35% via Batch ($0.067), 15% via Standard ($0.134).
For 4K resolution, multiply base costs by approximately 1.8:
| Monthly Volume | Standard Only | Batch Only | Hybrid Strategy | Annual Savings |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1,000 (4K) | $240 | $120 | $95 | $1,740 |
| 5,000 (4K) | $1,200 | $600 | $475 | $8,700 |
| 10,000 (4K) | $2,400 | $1,200 | $860 | $18,480 |
| 25,000 (4K) | $6,000 | $3,000 | $2,150 | $46,200 |
| 50,000 (4K) | $12,000 | $6,000 | $4,300 | $92,400 |
Break-even analysis favors batch for most use cases. Even at just 1,000 images monthly, switching from standard to batch saves $804 annually with zero additional effort beyond implementation. The hybrid approach requires more infrastructure but delivers an additional $144 annual savings at this volume—marginal but meaningful as you scale.
Volume discounts stack with batch savings. Enterprise agreements with Google often include additional percentage discounts on top of batch pricing. A 20% enterprise discount on batch pricing yields effective rates of $0.054/2K and $0.096/4K—approaching third-party pricing with official support.
The efficiency threshold sits around 500 images monthly. Below this level, the engineering effort to implement batch processing may not justify savings. Above this threshold, batch implementation pays for itself within the first month.
Quick Start and Recommendations
Getting started takes less than 30 minutes with the right approach. Follow this streamlined path to batch processing implementation.
Step 1: Audit your current usage. Review your image generation patterns over the past month. Categorize requests by urgency: how many truly require immediate delivery versus could tolerate next-day processing? Most teams discover 50-70% of their volume has flexible timing.
Step 2: Set up your development environment. Install the latest SDK version:
bash# Python pip install -U "google-genai>=1.52.0" # Node.js npm install @google/generative-ai@latest
Step 3: Implement a simple batch job. Start with a test batch of 10-50 images to validate your pipeline before scaling. Monitor completion times to calibrate expectations for your use case.
Step 4: Integrate batch scheduling into your workflow. Set up a daily batch job that collects non-urgent requests throughout the day and submits them overnight. This single change captures the majority of available savings.
Specific recommendations by user type:
For startups and small teams (under 5,000 images/month): Start with pure batch processing for maximum simplicity. The $2,000-4,000 annual savings funds other growth initiatives. Implement hybrid only when you have specific real-time requirements.
For mid-size companies (5,000-25,000 images/month): The hybrid approach delivers optimal value. Integrate laozhang.ai for bulk non-critical work, batch for scheduled quality-critical content, and reserve standard API for user-facing features. Expected savings: $15,000-50,000 annually.
For enterprise operations (25,000+ images/month): Negotiate volume discounts with Google directly while implementing hybrid architecture. Consider reserved capacity agreements for predictable high-volume workloads. Savings potential exceeds $100,000 annually at scale.
The path forward is clear: batch processing delivers immediate 50% savings with minimal implementation effort. Adding third-party providers for appropriate workloads pushes total savings to 60%+. Start with batch, measure your results, then expand to hybrid based on your specific requirements.
Your images await—at half the cost.