OpenClaw is a free, open-source AI assistant that transforms Telegram into a powerful personal AI command center. With 171k GitHub stars and support for models like Claude, GPT-4o, and Gemini, it runs locally on your machine and connects to Telegram so you can chat with AI from any device. Setup takes about 15 minutes, and this guide covers everything from installation to advanced deployment — the only resource you need to get your personal AI bot running on Telegram.
What Is OpenClaw and Why Telegram?
OpenClaw started as a side project by Peter Steinberger in November 2025, and in just over two months it has exploded to 171k stars on GitHub with 27.6k forks and 38 releases (GitHub, verified February 7, 2026). The project positions itself as "the AI that actually does things" — not just another chatbot wrapper, but a full AI assistant that can browse the web, control your computer, manage files, execute code, and maintain persistent memory across conversations. What makes OpenClaw different from tools like ChatGPT or Claude's native apps is that it runs locally on your hardware, giving you complete control over your data while still connecting to any cloud AI model you prefer.
The Telegram integration is where OpenClaw truly shines for everyday use. While OpenClaw supports over 50 channels including Discord, WhatsApp, and Slack, Telegram offers the best combination of features for a personal AI assistant. Telegram's bot API is completely free with no message limits, it supports rich formatting including code blocks and inline keyboards, and it works seamlessly across phones, tablets, desktops, and the web. Unlike WhatsApp which requires business accounts for bots, or Discord which is designed around servers and communities, Telegram's one-on-one bot chat feels natural — like texting a knowledgeable friend who happens to have access to the world's most powerful AI models.
The practical benefit is immediate: once connected, you can message your AI bot from your phone while commuting, send it documents to analyze, ask it to summarize articles, generate code snippets, or even control your home computer remotely. Your conversation history persists thanks to OpenClaw's built-in memory system, so your bot remembers context from previous chats. For teams and communities, OpenClaw supports Telegram group chats, forum topics, and multi-agent setups where different bots handle different tasks within the same group.
Prerequisites — What You Need Before Starting
Before diving into the installation, getting a few things ready upfront will save you from the frustrating experience of hitting an error halfway through the process. The requirements are minimal, but each one matters — missing even one will cause the setup to fail with cryptic error messages that waste your time diagnosing.
Node.js 22 or higher is the most critical requirement, and it is the one that trips up most people. OpenClaw is built on modern JavaScript features that require Node.js 22+, so older versions like Node 18 or 20 will not work (docs.openclaw.ai, verified February 7, 2026). You can check your current version by running node --version in your terminal. If you need to upgrade, the easiest approach is using a version manager like nvm on macOS/Linux or fnm on Windows. Run nvm install 22 and nvm use 22 to switch. On macOS, brew install node@22 also works. If you see a version below 22, do not skip this step — the installer will fail silently or throw confusing module-not-found errors that look unrelated to your Node version.
A Telegram account is obviously required, and you will need the Telegram app installed on at least one device where you can interact with @BotFather. Desktop or mobile both work. If you do not have Telegram yet, download it from telegram.org — account creation takes about one minute and requires only a phone number for verification.
An AI model API key is needed to power your bot's intelligence. OpenClaw does not include its own AI model — it connects to external providers like Anthropic (Claude), OpenAI (GPT-4o), or Google (Gemini). The good news is that Google's Gemini API offers a generous free tier that is perfect for getting started, so you can test everything without spending a cent. We will cover model selection in detail in a later section, but having at least one API key ready before you begin streamlines the initial setup considerably.
System requirements are modest: OpenClaw runs on macOS (Apple Silicon and Intel), Linux (Ubuntu 20.04+, Debian 11+), and Windows 10/11. It needs about 500MB of disk space and 512MB of RAM during operation. If you plan to run it on a server for 24/7 availability, a basic VPS with 1GB RAM is sufficient — we cover server deployment in a dedicated section later.
Step-by-Step OpenClaw Installation

The installation process differs slightly by operating system, but the core approach is the same: run a one-line installer that handles all dependencies, then initialize OpenClaw with its guided onboarding. The entire process takes about three minutes on a typical internet connection, and the installer is smart enough to detect your system and configure everything automatically.
Installing on macOS and Linux is the simplest path. Open your terminal and run the official install script. This downloads the latest OpenClaw binary, adds it to your PATH, and verifies the installation in one step. After the script completes, you should see a success message confirming the version number. As of February 7, 2026, the latest version is 2026.2.6, which includes significant improvements to the Telegram integration including better handling of media messages and inline keyboards.
bashcurl -fsSL https://openclaw.ai/install.sh | bash
After the base installation, run the onboarding wizard which guides you through initial configuration including daemon setup. The daemon is what keeps OpenClaw running in the background and is essential for Telegram connectivity — without it, your bot would only work while your terminal is open.
bashopenclaw onboard --install-daemon
The onboarding wizard asks a series of questions: which AI provider to use as default, whether to enable the web browser integration, and whether to install the background daemon. For Telegram use, always answer yes to the daemon question. The wizard creates a configuration directory at ~/.openclaw/ where all your settings, conversation history, and API keys are stored.
Installing on Windows uses PowerShell instead of bash. Open PowerShell as Administrator (right-click the Start button and select "Windows PowerShell (Admin)") and run the Windows-specific installer. The process is equivalent to the macOS/Linux version but uses Windows service management instead of a Unix daemon.
powershellirm https://openclaw.ai/install.ps1 | iex
Then run the same onboarding command in a new PowerShell window (regular, not admin):
powershellopenclaw onboard --install-daemon
Installing with Docker is the recommended approach if you want a clean, isolated installation or plan to deploy on a server. Docker handles all dependencies automatically and makes updates as simple as pulling a new image. Create a docker-compose.yml file in a new directory and start the container. The Docker approach is particularly good for server deployment, which we cover in detail later.
yamlversion: '3.8' services: openclaw: image: ghcr.io/openclaw/openclaw:latest container_name: openclaw restart: unless-stopped ports: - "18789:18789" volumes: - ./data:/root/.openclaw environment: - NODE_ENV=production
bashdocker compose up -d
After installation by any method, verify everything works by running openclaw --version — you should see 2026.2.6 or later. If the command is not found, close and reopen your terminal to reload your PATH environment variable. On Windows, you may need to restart PowerShell completely.
Creating and Connecting Your Telegram Bot
Creating a Telegram bot is entirely handled through Telegram itself, using a special bot called @BotFather that manages bot creation and configuration. The process involves a simple conversation — no coding, no API calls, no dashboards to navigate. It takes about two minutes and gives you a unique API token that OpenClaw uses to control your bot.
Step 1: Start a chat with @BotFather. Open Telegram and search for @BotFather (make sure it has the blue verified checkmark). Tap "Start" to begin the conversation. BotFather is Telegram's official bot management interface and has been the standard way to create bots since Telegram introduced its bot platform. Every legitimate Telegram bot starts here.
Step 2: Create a new bot. Send the command /newbot to BotFather. It will ask you two questions in sequence. First, it asks for a display name — this is what users see as the bot's name in their chat list. You can use spaces and special characters here, something like "My AI Assistant" or "OpenClaw Bot" works well. Second, it asks for a username — this must end in "bot" (like my_openclaw_bot or PersonalAIBot) and must be unique across all of Telegram. If your first choice is taken, try adding numbers or underscores.
Step 3: Save your API token. After you provide both names, BotFather responds with a message containing your bot's API token. It looks something like 7123456789:AAHx0rJ9GdF2mVN6KwZ8sE5yRtQp3LbCfWk. This token is essentially the password to your bot — anyone with this token can control your bot, read its messages, and send messages on its behalf. Copy it immediately and store it somewhere safe. Never share it publicly or commit it to a public repository.
Step 4: Connect OpenClaw to Telegram. Now switch back to your terminal. Use the OpenClaw CLI to add Telegram as a provider and paste in your bot token. The --provider telegram flag tells OpenClaw you are setting up a Telegram connection specifically, and the --token flag passes your BotFather token.
bashopenclaw-cli providers add --provider telegram --token YOUR_BOT_TOKEN
OpenClaw validates the token by making a test API call to Telegram's servers. If the token is valid, you will see a confirmation message with your bot's username. If you get an error, double-check that you copied the entire token including the colon in the middle — a common mistake is accidentally cutting off the first or last few characters.
Step 5: Pair your account. Open Telegram and find your newly created bot (search for the username you chose). Send any message to it — "hello" works fine. OpenClaw will detect this as an unpaired device and respond with a pairing code, typically a 6-digit number. Back in your terminal, approve the pairing request:
bashopenclaw-cli pairing approve
This links your Telegram account to your OpenClaw instance so only you (and accounts you explicitly approve) can use the bot. The pairing system is a security feature that prevents random Telegram users from using your bot and burning through your API credits. After pairing, send another message to your bot — this time it should respond with an actual AI-generated reply. If it does, congratulations: your personal AI bot is live on Telegram.
Choosing the Right AI Model for Your Bot
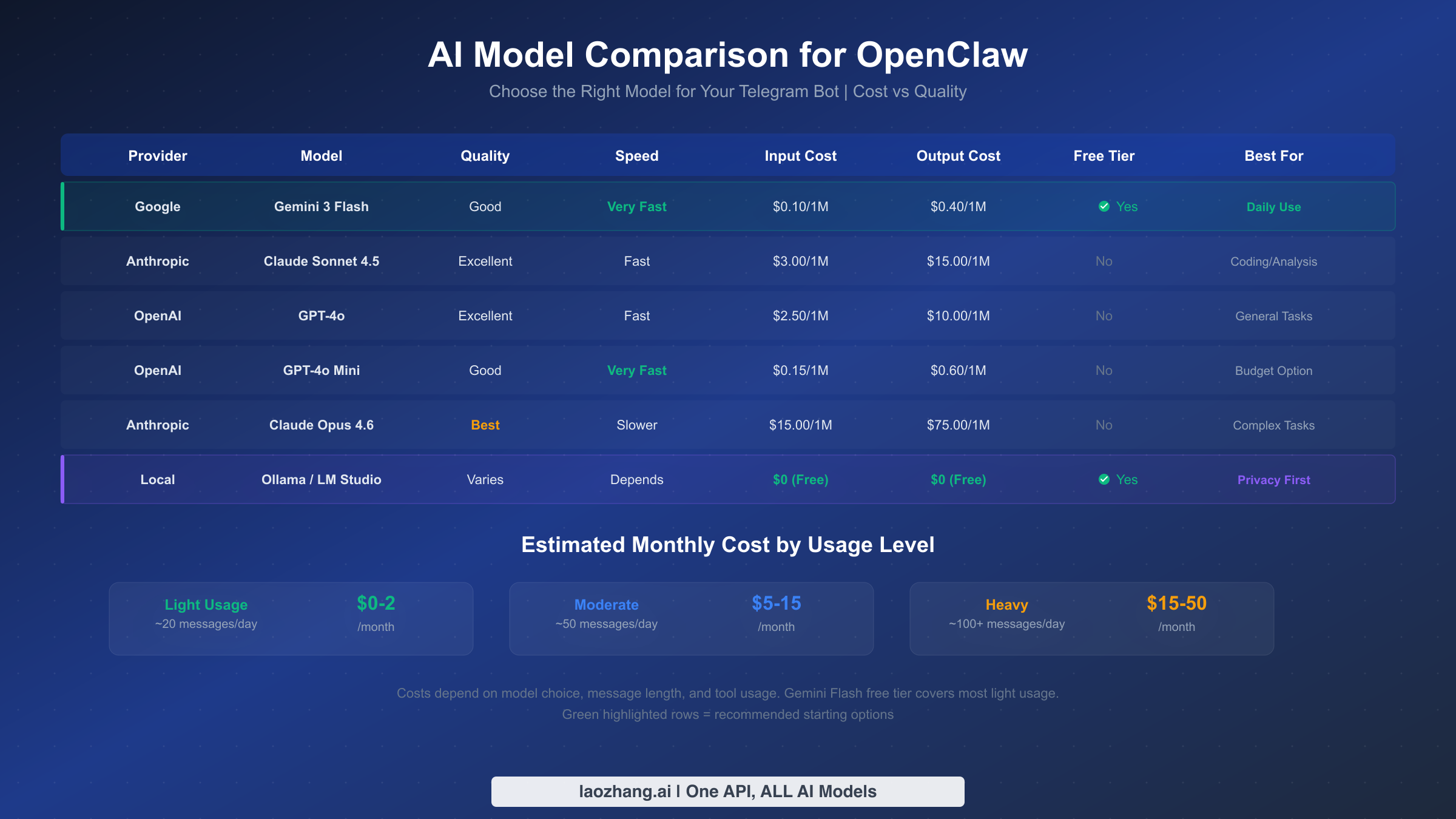
Selecting the right AI model is one of the most consequential decisions you will make during setup, because it directly determines three things your daily experience depends on: how intelligent your bot's responses are, how fast those responses arrive, and how much you pay each month. Most OpenClaw tutorials skip this entirely, leaving users on whatever default was configured during onboarding. But spending five minutes understanding your options can save you significant money while getting better results.
OpenClaw supports virtually every major AI provider through a unified interface, which means switching models is as simple as changing a configuration value — you are never locked in. The command openclaw model set <model-name> changes your default model instantly, and you can even switch mid-conversation using the Telegram command /model. Here is how the most popular options compare for Telegram bot use, based on current pricing verified against official documentation as of February 7, 2026.
Google Gemini 2.0 Flash is the strongest recommendation for most users starting out, and the reason is simple: it is free. Google's free tier provides 60 requests per minute and 1 million tokens per day through AI Studio at no cost (ai.google.dev, verified February 7, 2026). For a personal Telegram bot handling casual conversations, questions, and light tasks, most users will never exceed these limits. The quality is surprisingly good — Gemini Flash responses are fast (typically under 2 seconds), coherent, and handle most everyday tasks well. The trade-off is that complex reasoning, nuanced analysis, and creative writing are noticeably weaker compared to premium models. To configure it, get your Gemini API key from Google AI Studio and set it in OpenClaw:
bashopenclaw config set gemini_api_key YOUR_KEY openclaw model set gemini-2.0-flash
Claude Sonnet 4.5 from Anthropic hits the sweet spot between quality and cost for users who want noticeably better responses than Gemini Flash but do not need the absolute best. Claude excels at nuanced conversation, accurate summarization, and following complex instructions — qualities that matter when your bot handles real work tasks through Telegram. At approximately $3 per million input tokens and $15 per million output tokens (Anthropic pricing page, verified February 7, 2026), a moderate user sending 50-100 messages per day can expect to spend $5-15 per month. To set up Claude, get your Claude API key and configure it:
bashopenclaw config set anthropic_api_key YOUR_KEY openclaw model set claude-sonnet-4-5
GPT-4o from OpenAI remains a strong all-around choice, particularly for users already invested in the OpenAI ecosystem. It handles code generation, data analysis, and multilingual tasks well, with pricing at $2.50 per million input tokens and $10 per million output tokens (OpenAI API pricing page, verified February 7, 2026). GPT-4o's speed is competitive with Claude Sonnet, and its knowledge base is frequently updated. For setup, get your OpenAI API key and configure:
bashopenclaw config set openai_api_key YOUR_KEY openclaw model set gpt-4o
Local models via Ollama offer a completely free, completely private option for users with capable hardware. If your machine has at least 16GB of RAM (32GB preferred for larger models), you can run models like Llama 3, Mistral, or Qwen locally through Ollama integration. The quality varies dramatically by model size — 7B parameter models handle simple Q&A but struggle with complex tasks, while 70B+ models rival cloud offerings. The main advantage is zero API costs and complete data privacy. The trade-off is slower response times (5-30 seconds depending on hardware) and significant CPU/GPU usage.
For users who want access to multiple models through a single API endpoint — which is particularly convenient when you want to switch between Claude, GPT, and Gemini without managing separate API keys — services like laozhang.ai provide a unified interface that simplifies configuration. Instead of setting up three separate API keys, you configure one endpoint that routes to whichever model you select, and you get consolidated billing across all providers.
Practical monthly cost estimates help put this in perspective. A light user (10-20 messages per day, mostly short questions) will spend $0-2 per month using Gemini Flash free tier or about $2-5 with Claude or GPT. A moderate user (50-100 messages per day, mix of short and long interactions) should budget $5-15 per month with premium models. A heavy user (200+ messages, long documents, code generation) might see $15-50 per month. These estimates assume typical message lengths and include both input and output tokens.
Advanced Telegram Features and Commands
Once your basic setup is working, OpenClaw's Telegram integration unlocks a rich set of features that transform the experience from a simple chat interface into a full-featured AI command center. These features are what separate OpenClaw from basic chatbot wrappers — they leverage Telegram's native capabilities in ways that make your AI assistant genuinely more useful in daily life.
Built-in commands give you quick control over your bot without navigating any settings menu. The most important ones to learn are /status which shows your current model, token usage, and system health; /reset which clears the conversation context when your bot gets confused or you want to start fresh; /model which lets you switch between AI models on the fly; and /help which lists all available commands. OpenClaw registers these as Telegram's native bot commands, meaning they appear in the autocomplete menu when you type / in the chat — no need to memorize them.
Sending and receiving files works naturally through Telegram's built-in file sharing. Drop a PDF into the chat and ask your bot to summarize it. Send a photo and ask for a description or analysis. Share a code file and ask for a review. OpenClaw automatically processes these attachments using multi-modal AI capabilities, so interactions feel as natural as sending files to a colleague. Supported formats include PDF, images (JPEG, PNG, WebP), text files, and common document formats. File size limits follow Telegram's standard limits — 50MB for regular messages, 2GB for documents sent via the Telegram API.
Group chat integration is where things get particularly interesting for teams and communities. You can add your OpenClaw bot to any Telegram group, and it will respond when mentioned by username or when messages match configured triggers. The key configuration setting is TELEGRAM_GROUP_BEHAVIOR which controls how the bot interacts in groups — "mention" means it only responds when tagged with @username, "reply" means it responds to messages that reply to its previous messages, and "all" means it reads and can respond to every message (use carefully in active groups). Configure this in your OpenClaw settings:
bashopenclaw config set telegram_group_behavior mention
Forum topics in Telegram supergroups are supported natively by OpenClaw, allowing different conversation threads within a single group. For example, a team could have a "Code Review" topic where the bot reviews PRs, a "Research" topic where it summarizes papers, and a "General" topic for casual questions. Each topic maintains its own conversation context, so the bot does not confuse discussions across topics. Enable this with openclaw config set telegram_forum_topics true.
Multi-agent setups are an advanced feature where multiple OpenClaw instances (each with different configurations or models) operate as separate bots in the same Telegram group. Imagine having a "Coder" bot running Claude Opus for complex programming tasks and a "Researcher" bot running Gemini Flash for quick fact-checking, both in the same workspace. Each bot has its own Telegram token and OpenClaw instance, and you address them by their respective usernames. This requires running multiple OpenClaw processes, which is most practical with Docker Compose where each bot is a separate service.
Inline keyboard buttons appear below bot messages and provide quick-action controls. OpenClaw uses these for features like "Regenerate" (get a different response), "Continue" (extend a truncated response), and "Switch Model" (change AI model for the next response). These buttons make interaction faster than typing commands and give the bot a polished, professional feel. They are enabled by default and require no additional configuration.
Running OpenClaw 24/7 on a Server
Running OpenClaw on your local machine works perfectly for testing and casual use, but it has an obvious limitation: your bot goes offline whenever your computer sleeps, shuts down, or loses internet connectivity. For users who rely on their AI bot throughout the day — checking it from their phone during commutes, sending quick questions during meetings, or using it from multiple devices — deploying OpenClaw to a server provides the always-on reliability that makes the bot truly useful as a daily tool.
VPS deployment with Docker is the most common and recommended approach. A basic VPS from providers like Hetzner, DigitalOcean, or Linode costs $4-6 per month for a 1GB RAM instance, which is more than enough for a single OpenClaw deployment serving one to five users. Docker simplifies the deployment dramatically because it packages OpenClaw with all its dependencies into a single container that runs identically on any Linux server. Start by getting a VPS with Ubuntu 22.04 or later, then install Docker and Docker Compose:
bashsudo apt update && sudo apt install -y docker.io docker-compose-plugin sudo systemctl enable docker
Create a project directory and the Docker Compose configuration file. The key environment variables are your AI model API keys and the Telegram bot token. Using a .env file keeps sensitive values out of your compose file, which is important if you version-control your deployment configuration.
bashmkdir -p ~/openclaw && cd ~/openclaw
Create a .env file with your credentials:
ANTHROPIC_API_KEY=your_anthropic_key
OPENAI_API_KEY=your_openai_key
GEMINI_API_KEY=your_gemini_key
TELEGRAM_BOT_TOKEN=your_telegram_bot_token
Your docker-compose.yml should reference these environment variables and mount a persistent data volume so conversation history and settings survive container restarts:
yamlversion: '3.8' services: openclaw: image: ghcr.io/openclaw/openclaw:latest container_name: openclaw restart: unless-stopped env_file: .env volumes: - ./data:/root/.openclaw ports: - "18789:18789"
Launch with docker compose up -d and your bot is running. Check logs with docker compose logs -f openclaw to confirm it connected to Telegram successfully. The restart: unless-stopped policy ensures your bot automatically recovers after server reboots or crashes.
Cloud platform deployment offers an even simpler alternative for users who prefer managed infrastructure. Platforms like Zeabur and Render provide one-click OpenClaw deployment templates that handle Docker, SSL, and automatic restarts without any server management. Zeabur is particularly popular in the OpenClaw community because it offers a free tier that can run a single instance indefinitely. The trade-off is less control over the underlying infrastructure and potential cold-start delays on free tiers.
Updating your deployment is straightforward with Docker. When a new OpenClaw version releases, pull the latest image and restart:
bashcd ~/openclaw docker compose pull docker compose up -d
Your configuration, conversation history, and paired devices are preserved in the mounted data volume. OpenClaw publishes frequent updates — 38 releases since November 2025 (GitHub, verified February 7, 2026) — so checking for updates monthly keeps you on the latest features and security patches.
Security Best Practices and Cost Management

Running an AI assistant that connects to external APIs and processes your messages requires thoughtful security practices, especially when that assistant is accessible from your phone through a public messaging platform. Similarly, understanding and controlling your costs prevents the unpleasant surprise of an unexpected API bill at the end of the month. Most OpenClaw guides treat these as afterthoughts, but for anyone using this in a real daily workflow, they deserve dedicated attention.
Token security is your first line of defense. Your Telegram bot token and AI provider API keys are the most sensitive values in your setup. Never store them in plain text files that might get backed up to cloud services, committed to Git repositories, or left readable by other users on shared systems. On a VPS, use environment variables loaded from a .env file with restricted permissions (chmod 600 .env). On a local machine, OpenClaw stores keys in ~/.openclaw/config.json which inherits your user account's file permissions — verify this file is not world-readable with ls -la ~/.openclaw/config.json.
Pairing control determines who can use your bot and is the primary mechanism preventing unauthorized usage. By default, OpenClaw requires explicit approval for each new device that tries to interact with your bot. Keep this strict — if someone discovers your bot's username and sends it a message, the pairing system blocks them from getting any AI responses. Periodically review your paired devices with openclaw-cli pairing list and revoke any you do not recognize with openclaw-cli pairing revoke <id>. If you suspect your bot token has been compromised, immediately generate a new one through @BotFather (send /revoke followed by /newbot or use /token to regenerate) and update your OpenClaw configuration.
API key spending limits are available from all major providers and are the most effective way to prevent runaway costs. Anthropic, OpenAI, and Google all allow you to set monthly spending caps in their dashboards. Set these to match your budget — for a personal bot, $20-30 per month covers generous usage with premium models. Even if your bot goes haywire or someone bypasses pairing (unlikely but possible), the spending cap stops charges at your predetermined limit. OpenAI lets you set both soft limits (email warnings) and hard limits (service stops) at api.openai.com/account/billing. Anthropic offers similar controls in the console at console.anthropic.com. For users accessing multiple models through a unified provider like laozhang.ai, you get consolidated spending controls across all models from a single dashboard.
Monthly cost estimation helps set appropriate limits. Based on typical Telegram usage patterns, here is what to expect at different activity levels. A light user sending 10-20 short messages per day using Gemini Flash free tier pays nothing — Google's free tier of 1 million tokens per day is more than sufficient. A moderate user sending 50-100 messages daily with Claude Sonnet 4.5 should budget $8-15 per month, assuming an average of 500 input tokens and 1,000 output tokens per message exchange. A heavy user running 200+ daily interactions with document analysis and code generation could see $30-50 per month with premium models. Adding VPS hosting ($5/month) to any tier gives you 24/7 availability. The key insight is that starting with Gemini Flash (free) lets you test and refine your workflow before committing to paid models.
Network security on servers matters too. If you are running OpenClaw on a VPS, the web interface on port 18789 should not be exposed to the public internet unless you need remote access. Use a firewall to restrict access: sudo ufw allow ssh && sudo ufw enable on Ubuntu blocks all incoming traffic except SSH by default. If you do need remote web access to the OpenClaw dashboard, set up a reverse proxy with Nginx and SSL via Let's Encrypt rather than exposing the port directly. The Telegram bot communication itself goes through Telegram's servers using outbound HTTPS connections, so no inbound ports need to be open specifically for the bot to function.
Troubleshooting Common Issues
Even with careful preparation, setup issues happen — and the faster you can identify and fix them, the less frustrating the experience. The problems below represent the most common issues reported in the OpenClaw community, along with their solutions. Most can be resolved in under a minute once you know what to look for.
"Command not found: openclaw" after installation is almost always a PATH issue. The installer adds OpenClaw to your PATH, but your current terminal session does not pick up the change until you reload it. Close your terminal completely and open a new one — do not just open a new tab in the same terminal app, as some terminals share environment state across tabs. If the command still is not found, check that the install directory is in your PATH by running echo $PATH and looking for the OpenClaw binary location (typically ~/.openclaw/bin or /usr/local/bin). On Windows, restarting PowerShell or even logging out and back in may be required.
"Error: Node.js version X.X is not supported" means your Node.js version is below the required 22+. This is the single most common setup failure. Run node --version to confirm your version. If you have multiple Node versions installed through nvm, make sure you have activated the correct one with nvm use 22. A subtle trap: some systems have a system-wide Node installation that shadows the nvm version — running which node shows which binary is actually being used.
Bot not responding to messages after pairing could indicate several things. First, verify the daemon is running: openclaw status should show "daemon: running." If it shows stopped, start it with openclaw daemon start. Second, check that your AI provider API key is valid — an expired or revoked key causes silent failures where OpenClaw receives your message but cannot generate a response. Test your API key independently: openclaw test-connection verifies connectivity to your configured provider. Third, check Telegram's API status — while rare, Telegram's bot API occasionally experiences delays during high-traffic periods.
"Error: Telegram token invalid" during provider setup means the token you pasted does not match BotFather's format or has been revoked. The token format is NUMBERS:ALPHANUMERIC_STRING with exactly one colon separating two parts. Common mistakes include copying extra whitespace before or after the token, accidentally including the surrounding text from BotFather's message, or using an old token that was revoked when you generated a new one. Go back to your BotFather chat, find the most recent token message, and carefully copy only the token string.
Pairing code not appearing when you message your bot usually means the Telegram provider was not properly added. Run openclaw-cli providers list to verify Telegram appears in the list. If it does not, re-run the providers add command from the setup step. If Telegram is listed but the bot still does not respond, check the OpenClaw logs for errors: openclaw logs --tail 50 shows the most recent log entries, which typically reveal the exact error — common culprits include network timeouts, DNS resolution failures on VPS deployments, or rate limiting during initial setup.
High memory usage or slow responses can occur when running larger AI models locally through Ollama or when conversation context grows very long. OpenClaw maintains conversation context in memory, and after hundreds of messages, this context can consume significant RAM and cause the AI to respond slowly as it processes a long history. The solution is the /reset command in Telegram, which clears the conversation context and starts fresh. For persistent memory (things the bot should always remember), use OpenClaw's memory feature: /remember I prefer responses in bullet points stores information that survives context resets.
Docker container crashes on startup usually point to insufficient resources or port conflicts. Check container logs with docker logs openclaw to see the specific error. The most common cause on small VPS instances is running out of memory — add swap space with sudo fallocate -l 1G /swapfile && sudo chmod 600 /swapfile && sudo mkswap /swapfile && sudo swapon /swapfile to provide a safety margin. Port 18789 conflicts are another common issue; if another service uses that port, change it in your docker-compose.yml by mapping to a different host port: "18790:18789".
Frequently Asked Questions
Is OpenClaw completely free to use? OpenClaw itself is 100% free and open-source under a permissive license. The only costs come from the AI model API you choose to connect — and even those can be free if you use Google Gemini's free tier, which provides 60 requests per minute and 1 million tokens per day at no charge (ai.google.dev, verified February 7, 2026). Running on your own machine costs nothing additional. Running on a VPS for 24/7 availability adds $4-6 per month for hosting.
What makes OpenClaw different from just using ChatGPT or Claude directly? Three things: first, OpenClaw runs locally and gives you complete data privacy — your conversations stay on your machine, not on a third-party server. Second, it supports any AI model through a single interface, so you can switch between Claude, GPT, Gemini, and local models without changing apps. Third, its Telegram integration means you get AI assistance from any device without installing yet another app — Telegram is already on most people's phones.
Can I use OpenClaw in a Telegram group with multiple people? Yes, and this is one of its strongest features. Add the bot to any group, configure telegram_group_behavior to "mention" (safest for active groups), and every group member can interact with the bot by @mentioning it. Each user's interactions are tracked separately for context. For team workspaces, combine this with Telegram's forum topics feature to organize different types of AI interactions into dedicated threads.
How do I update OpenClaw to the latest version? For local installations, run openclaw update which downloads and installs the latest release automatically. For Docker deployments, run docker compose pull && docker compose up -d in your project directory. OpenClaw maintains backward compatibility between releases, so updates should not break your existing configuration or conversation history. Check the release notes on GitHub for any version-specific migration steps.
Does my bot work when my computer is off? Only if you have deployed OpenClaw to a server (VPS or cloud platform). When running on your local machine, the bot stops responding when your computer sleeps, shuts down, or loses internet. This is why the server deployment section recommends Docker on a VPS for users who want reliable, always-on access. The monthly cost of $4-6 for a basic VPS is well worth the convenience.
