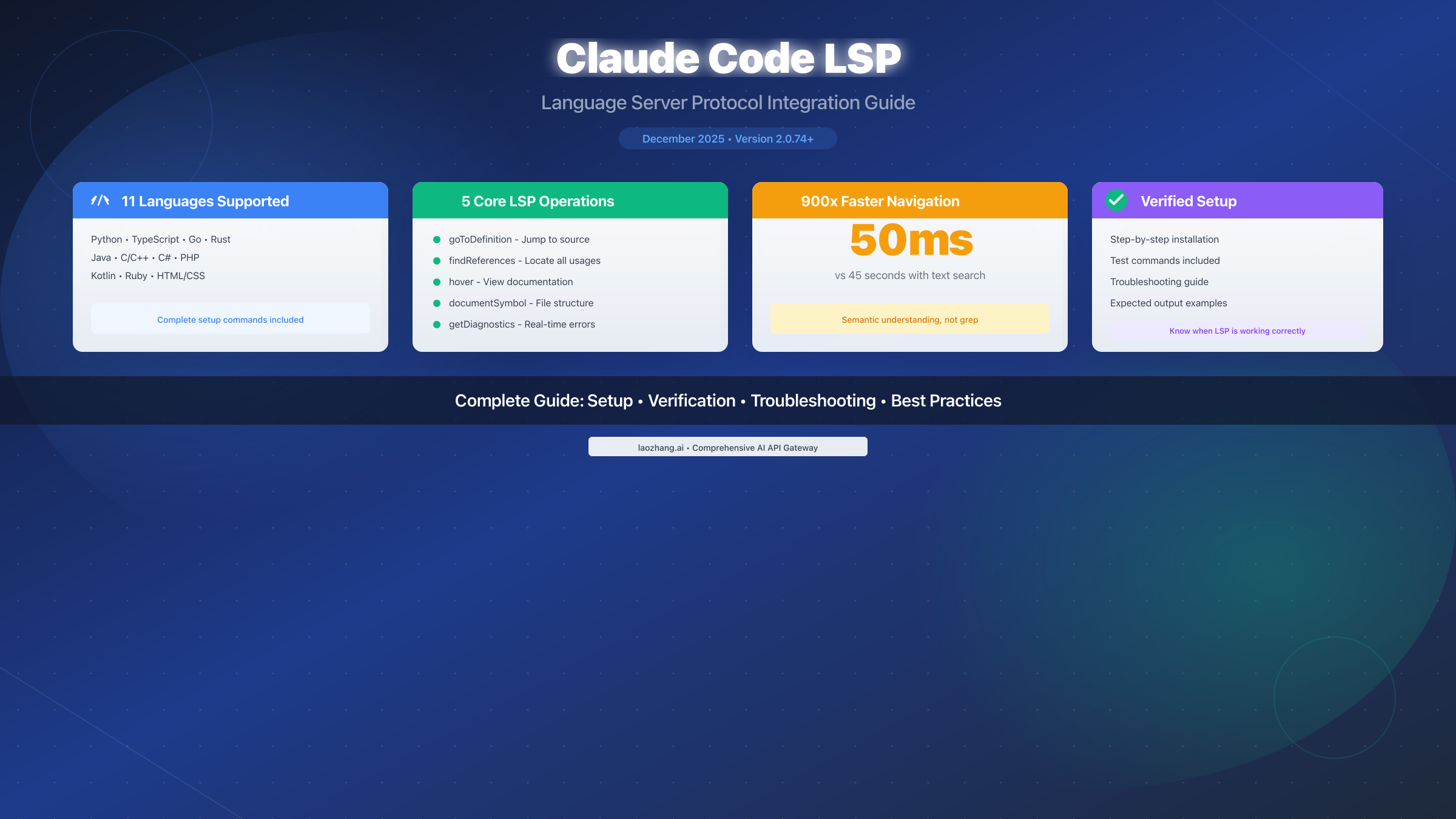
Claude Code LSP brings Language Server Protocol support to Anthropic's CLI coding assistant, enabling IDE-like code intelligence including go-to-definition, find references, and real-time diagnostics. Released in December 2025 with version 2.0.74, this feature supports 11 programming languages: Python, TypeScript, Go, Rust, Java, C/C++, C#, PHP, Kotlin, Ruby, and HTML/CSS. With LSP enabled, Claude Code navigates codebases in 50ms instead of 45 seconds using traditional text search, fundamentally transforming how developers interact with AI coding assistants.
This comprehensive guide walks you through everything from initial setup to advanced troubleshooting, ensuring you can leverage LSP capabilities regardless of your primary programming language.
What is Claude Code LSP? Understanding Language Server Protocol
Language Server Protocol represents one of the most significant advances in developer tooling of the past decade. Created by Microsoft in 2016, LSP establishes a standardized communication protocol between development tools and language servers, enabling rich code intelligence features to be built once and used across any editor or IDE that supports the protocol.
The core innovation of LSP lies in its decoupling of language intelligence from specific editors. Before LSP, every editor needed its own implementation for each programming language—a combinatorial explosion that limited innovation. With LSP, a single Python language server (like Pyright) works identically in VS Code, Neovim, Sublime Text, and now Claude Code.
When you hover over a function in your IDE and see its type signature, that's LSP at work. When you right-click "Go to Definition" and instantly jump to the source file, that's LSP. When you rename a variable and see every reference across your codebase update simultaneously, that's the power of semantic code understanding that LSP provides.
Claude Code's LSP integration, released in version 2.0.74 (December 2025), brings this same intelligence to terminal-based AI coding assistance. Rather than relying on text-based grep searches that can return false positives and take seconds to complete, Claude Code with LSP understands your code's semantic structure—knowing exactly where a function is defined, where it's called, and what types it expects.
The performance difference is striking: finding all call sites of a function takes approximately 50ms with LSP compared to 45 seconds with traditional text search. This 900x improvement transforms not just speed but workflow—you can ask Claude to analyze dependencies, refactor code, or understand call hierarchies without waiting.
For developers already familiar with installing Claude Code, adding LSP support is a natural next step that significantly enhances the tool's capabilities.
Quick Start: Enable LSP in 5 Minutes
Getting Claude Code LSP running requires three straightforward steps: enabling the LSP tool, adding a plugin marketplace, and installing your first language plugin. Most developers can complete this process in under five minutes.
Step 1: Enable the LSP Tool
The LSP feature requires explicit enablement through an environment variable. You have two options for this:
bashENABLE_LSP_TOOL=1 claude # Option B: Enable permanently (add to your shell profile) export ENABLE_LSP_TOOL=1
For permanent enablement, add the export line to your ~/.bashrc, ~/.zshrc, or equivalent shell configuration file. This ensures LSP capabilities are available every time you launch Claude Code.
Step 2: Add a Plugin Marketplace
Claude Code uses a marketplace system for plugin distribution. While the official Anthropic marketplace (claude-plugins-official) is automatically available, community marketplaces offer additional plugins and often faster updates:
bash# Add the boostvolt community marketplace /plugin marketplace add boostvolt/claude-code-lsps
This command registers the marketplace, making its plugins available for installation. You only need to run this once—the marketplace persists across sessions.
Step 3: Install Your First Language Plugin
With the marketplace added, install a plugin for your primary programming language:
bash# For Python developers /plugin install pyright@claude-code-lsps # For TypeScript/JavaScript developers /plugin install vtsls@claude-code-lsps # For Go developers /plugin install gopls@claude-code-lsps
The plugin system will attempt to auto-install the required language server binary. If auto-installation fails, you'll see instructions for manual installation in the /plugin Errors tab.
Immediate Verification
After installation, verify LSP is working by opening a project and running a simple test:
bash# In Claude Code, after opening a Python project > Can you go to the definition of the main function? # Expected: Claude navigates directly to the function definition # rather than searching through files
If Claude responds with specific file locations and line numbers rather than performing text searches, LSP is working correctly. For those exploring Claude Code's broader capabilities, the MCP plugin system provides additional extensibility options beyond LSP.
Language-by-Language Setup Guide
Each programming language requires its own LSP plugin and corresponding language server binary. This section provides complete setup instructions for all 11 supported languages, including both the Claude Code plugin command and the system-level binary installation.
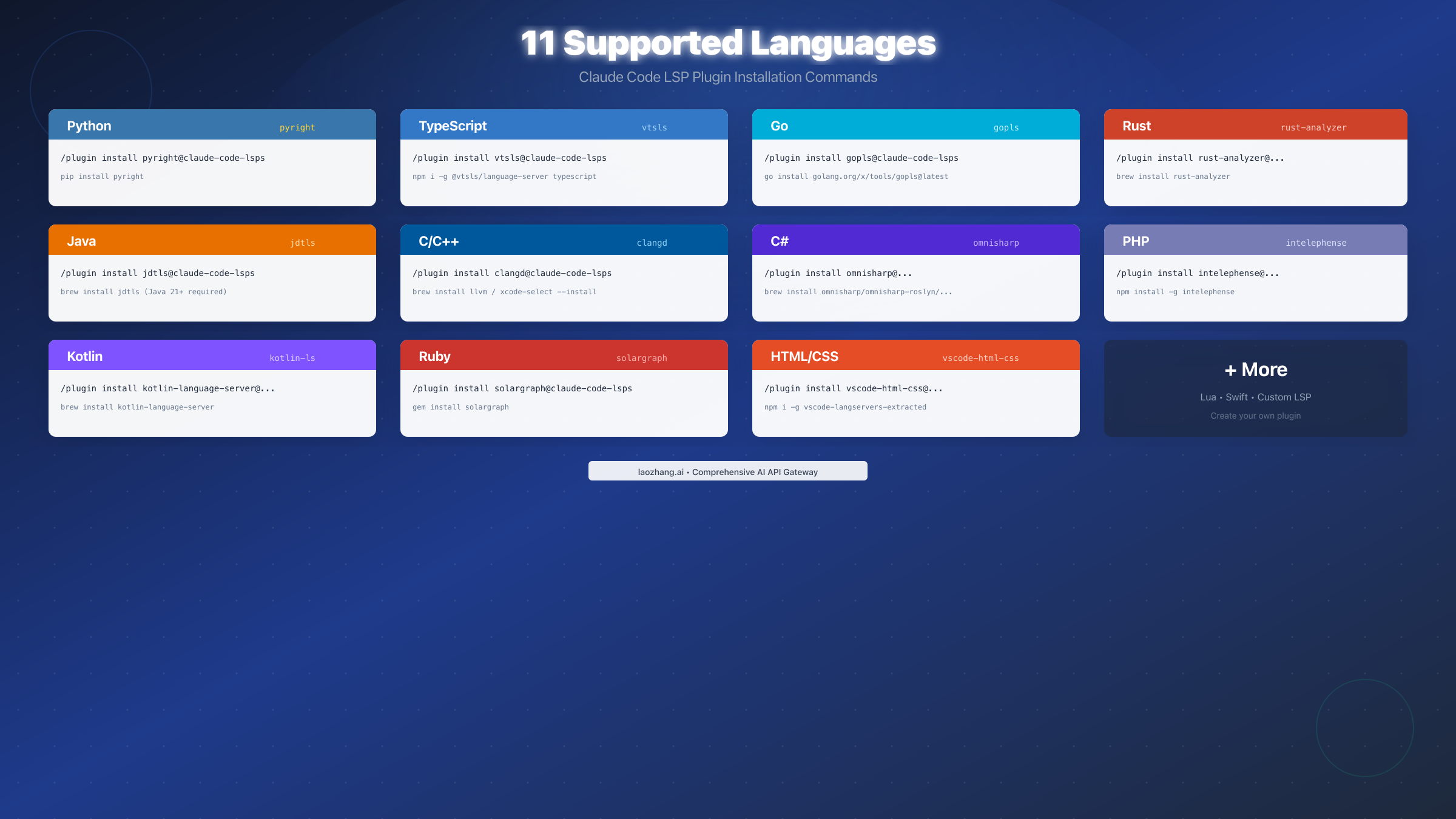
Python (Pyright)
Python developers benefit from Pyright's excellent type checking and fast performance. It's particularly effective for projects using type hints:
bash# Claude Code plugin /plugin install pyright@claude-code-lsps # System binary (choose one method) pip install pyright # or npm install -g pyright # or brew install pyright
Pyright reads your pyrightconfig.json or pyproject.toml for configuration. For optimal results, ensure your Python environment is properly configured in these files.
TypeScript and JavaScript (vtsls)
The vtsls server provides comprehensive TypeScript and JavaScript support, including JSDoc parsing for plain JavaScript projects:
bash# Claude Code plugin /plugin install vtsls@claude-code-lsps # System binary npm install -g @vtsls/language-server typescript
Note that TypeScript itself must be installed alongside vtsls for proper type resolution in TypeScript projects.
Go (gopls)
Google's official Go language server offers robust support for Go modules and workspaces:
bash# Claude Code plugin /plugin install gopls@claude-code-lsps # System binary go install golang.org/x/tools/gopls@latest
Ensure $GOPATH/bin is in your PATH for gopls to be discoverable. For Go workspaces with multiple modules, gopls handles cross-module navigation seamlessly.
Rust (rust-analyzer)
Rust-analyzer is the premier Rust language server, offering deep integration with Cargo and the Rust ecosystem:
bash# Claude Code plugin /plugin install rust-analyzer@claude-code-lsps # System binary (macOS) brew install rust-analyzer # System binary (via rustup) rustup component add rust-analyzer
For projects with complex Cargo configurations, rust-analyzer respects your Cargo.toml settings and handles workspace-level dependencies correctly.
Java (jdtls)
Eclipse's JDT Language Server provides Java support, requiring Java 21 or later:
bash# Claude Code plugin /plugin install jdtls@claude-code-lsps # System binary (macOS) brew install jdtls # Verify Java version java --version # Must be 21+
The jdtls server requires significant memory for large projects. Consider increasing your system's available RAM for optimal performance with enterprise Java codebases.
C and C++ (clangd)
LLVM's clangd provides excellent C/C++ support with fast indexing:
bash# Claude Code plugin /plugin install clangd@claude-code-lsps # System binary (macOS with LLVM) brew install llvm # or xcode-select --install # Includes clangd
For projects with complex build systems, create a compile_commands.json file using cmake, Bear, or your build tool's equivalent feature.
C# (OmniSharp)
Microsoft's OmniSharp server provides comprehensive .NET and C# support:
bash# Claude Code plugin /plugin install omnisharp@claude-code-lsps # System binary (macOS) brew install omnisharp/omnisharp-roslyn/omnisharp-mono
OmniSharp automatically detects .NET solutions and projects, providing navigation across the entire solution structure.
PHP (Intelephense)
Intelephense offers fast, feature-rich PHP intelligence:
bash# Claude Code plugin /plugin install intelephense@claude-code-lsps # System binary npm install -g intelephense
While Intelephense's free tier provides core functionality, a license unlocks additional features like code actions and workspace-wide renaming.
Kotlin (kotlin-language-server)
JetBrains-compatible Kotlin support:
bash# Claude Code plugin /plugin install kotlin-language-server@claude-code-lsps # System binary (macOS) brew install kotlin-language-server
The Kotlin language server works with both standalone Kotlin projects and mixed Java/Kotlin codebases.
Ruby (Solargraph)
Solargraph provides Ruby language intelligence with YARD documentation support:
bash# Claude Code plugin /plugin install solargraph@claude-code-lsps # System binary gem install solargraph
Run solargraph bundle in your project directory to index gems and enable comprehensive navigation.
HTML and CSS (vscode-langservers)
Web development language support:
bash# Claude Code plugin /plugin install vscode-html-css@claude-code-lsps # System binary npm install -g vscode-langservers-extracted
This package includes servers for HTML, CSS, and JSON, providing autocomplete and validation for web projects.
Verifying Your LSP Setup Works
After installing LSP plugins, verification ensures everything functions correctly before relying on these features in your workflow. This section provides specific test commands for each LSP operation.
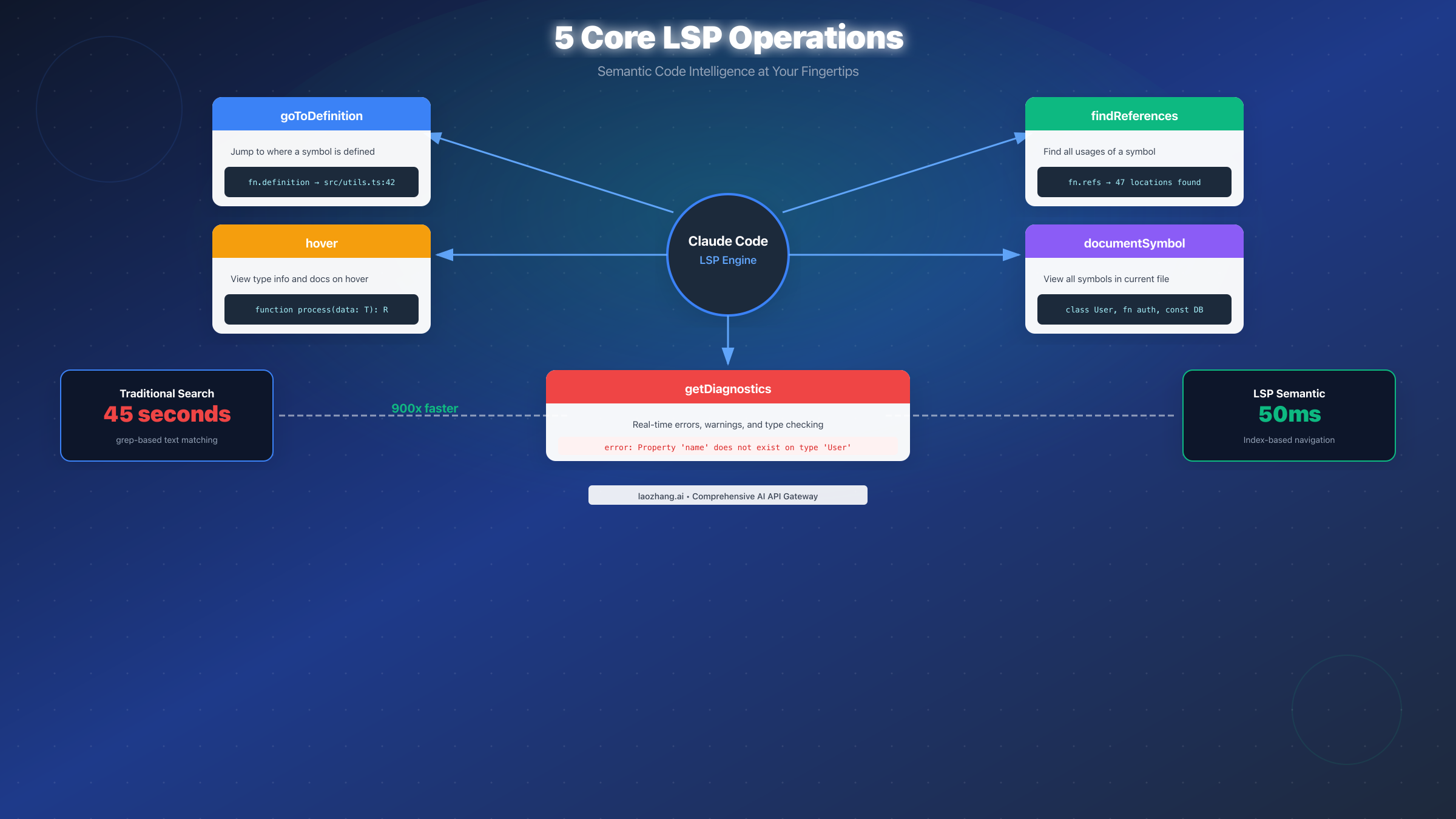
Testing goToDefinition
The goToDefinition operation should return precise file locations rather than search results:
bash# Test command in Claude Code > Go to the definition of [function_name] # Expected response format: "The function [name] is defined in src/utils/helpers.ts at line 42" # Red flag (indicates LSP not working): "I found several references to [name] in the following files..."
A working LSP setup provides exact locations immediately, while text-based fallback produces multiple potential matches that Claude then filters.
Testing findReferences
The findReferences operation should enumerate all usages with precise locations:
bash# Test command > Find all references to the [ClassName] class # Expected response format: "[ClassName] is referenced in 12 locations: - src/main.ts:15 (import statement) - src/services/auth.ts:8 (instantiation) - tests/auth.test.ts:4 (import) ..." # Red flag: "I'm searching through the codebase for [ClassName]..."
Testing hover Information
Hover provides type signatures and documentation without navigation:
bash# Test command > What is the type signature of the [function_name] function? # Expected response with LSP: "[function_name] is a function with signature: function processData(input: DataType, options?: Options): Promise<Result>" # Without LSP, Claude must read and parse the source file first
Testing diagnostics
Diagnostics surface errors and warnings in real-time:
bash# After making an intentional type error > Are there any type errors in the current file? # Expected response: "Yes, there's a type error on line 23: Type 'string' is not assignable to type 'number'"
Checking Plugin Status
Use the plugin management interface to verify installation:
bash# List installed plugins /plugin # Navigate to "Installed" tab to see active plugins # Check "Errors" tab for any loading issues
If plugins appear installed but LSP operations fail, the most common issue is a missing or incorrectly pathed language server binary. Proceed to the troubleshooting section for resolution steps.
Mastering LSP Operations
Beyond basic navigation, LSP operations enable sophisticated code analysis workflows when combined with Claude's reasoning capabilities. Understanding each operation's capabilities helps you leverage them effectively.
goToDefinition: Beyond Simple Navigation
While goToDefinition's basic use is jumping to function definitions, its power emerges in complex codebases with deep inheritance hierarchies or extensive module systems:
bash# Navigate through abstraction layers > Go to the definition of handleRequest, then show me its parent class definition # Trace type definitions > What's the definition of the ReturnType used in processData?
The semantic understanding means Claude can distinguish between a function named process in your code versus the same string appearing in comments or string literals—a common false-positive source in text-based searches.
findReferences: Understanding Code Impact
findReferences becomes essential for refactoring decisions:
bash# Assess refactoring impact > Find all references to the deprecated formatDate function. > How many unique files would be affected by changing its signature? # Understand usage patterns > Find references to the UserService class. > Categorize them by type: instantiation, method calls, or type annotations.
documentSymbol: File Structure Navigation
documentSymbol provides a hierarchical view of a file's structure:
bash# Get file overview > What classes, functions, and constants are defined in auth.service.ts? # Navigate large files > Show me all the public methods in the DatabaseConnection class
workspaceSymbol: Project-Wide Search
For finding symbols across an entire project:
bash# Find a class definition somewhere in the project > Find where the ConfigurationManager class is defined in this project # Locate interface definitions > Where is the PaymentProcessor interface defined?
Workflow Integration Tips
Effective LSP usage combines operations naturally:
bash# Comprehensive understanding workflow > I need to understand how authentication works in this codebase. > 1. Find the main auth-related classes using workspace symbol search > 2. Go to the AuthService definition > 3. Find all references to understand where it's used > 4. Check for any diagnostics or type errors in the auth module
This workflow, which might take 10-15 minutes of manual IDE navigation, completes in seconds with LSP-enabled Claude Code.
Troubleshooting Common Issues
Despite careful setup, LSP issues can arise from environment configuration, binary paths, or plugin state. This section addresses the most common problems with verified solutions.
"No LSP server available for file type"
This error indicates Claude Code cannot find a matching LSP plugin for your file type:
bash# Verify plugin is installed /plugin # Check "Installed" tab for your language's plugin # If missing, install it /plugin install pyright@claude-code-lsps # If installed but still failing, check file extension mapping # Some plugins only activate for specific extensions
The most common cause is installing a plugin but not restarting Claude Code afterward. Exit and relaunch to ensure plugins load correctly.
"Executable not found in $PATH"
The language server binary isn't accessible to Claude Code:
bash# Verify binary exists and is in PATH which pyright # Should return a path which gopls which rust-analyzer # If command not found, install the binary pip install pyright # for Python # Verify PATH includes binary location echo $PATH # For Go, ensure GOPATH/bin is in PATH export PATH=$PATH:$(go env GOPATH)/bin
If binaries are installed but not found, check whether you're using a different shell configuration than Claude Code uses.
Plugin Installed But Not Working
Sometimes plugins install successfully but fail to activate:
bash# Clear plugin cache rm -rf ~/.claude/plugins/cache # Restart Claude Code exit claude # Reinstall the plugin /plugin uninstall pyright@claude-code-lsps /plugin install pyright@claude-code-lsps
LSP Server Crashes on Large Files
Some language servers struggle with very large files:
bash# For Pyright, increase memory limit export PYRIGHT_MEMORY_LIMIT=4096 # For rust-analyzer, similar configuration via settings
Consider splitting extremely large files or optimizing language server settings for your project's scale.
Diagnostics Not Updating
If error highlights don't update after edits:
bash# Force diagnostic refresh > Refresh diagnostics for the current file # Check if language server is responsive /plugin # Look for error indicators in the Errors tab
GitHub Issues Reference
For issues not covered here, the official Claude Code repository tracks known problems:
- Issue #14803: LSP plugins not recognized despite correct configuration
- Issue #15359: Official plugins missing implementation code
Checking recent issues often reveals workarounds before official fixes are released.
For development teams requiring reliable API access for testing alongside Claude Code, services like laozhang.ai provide aggregated multi-model API access with consistent pricing, which can be particularly useful when testing AI-assisted code generation at scale.
Claude Code LSP vs Alternatives
Understanding how Claude Code LSP compares to traditional IDE-based LSP implementations and competing AI coding tools helps inform your tooling decisions.
Claude Code LSP vs VS Code Native LSP
VS Code's LSP implementation remains the gold standard for IDE-based development:
| Feature | Claude Code LSP | VS Code LSP |
|---|---|---|
| Supported Languages | 11 | 100+ |
| Setup Complexity | Medium | Low (extensions) |
| AI Integration | Native | Via extensions |
| Terminal-Native | Yes | No |
| Context Window | 200K tokens | N/A |
VS Code wins on breadth of language support and setup simplicity, while Claude Code's advantage lies in AI-native integration where LSP information feeds directly into reasoning about your code.
Claude Code vs Cursor
Cursor, built on VS Code, offers a different approach to AI-assisted development:
| Aspect | Claude Code | Cursor |
|---|---|---|
| Interface | Terminal CLI | Full IDE |
| LSP Depth | 5 operations | Full VS Code LSP |
| AI Model | Claude (any version) | Multiple models |
| Context | 200K+ tokens | Varies by model |
| Price | Usage-based | $20/month Pro |
Cursor excels for developers preferring GUI-based development, while Claude Code suits terminal-native workflows and scenarios requiring deep codebase analysis within conversations.
For a deeper comparison of IDE features, see our Claude Code UI integration guide.
Claude Code vs GitHub Copilot
GitHub Copilot focuses on inline code suggestions rather than LSP-based navigation:
| Feature | Claude Code + LSP | GitHub Copilot |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Mode | Conversational + Navigation | Inline Suggestions |
| Codebase Understanding | Full LSP navigation | Limited context |
| Refactoring | Semantic-aware | Pattern-based |
| Platform | Terminal | IDE extensions |
These tools often complement rather than replace each other—Copilot for rapid inline suggestions, Claude Code for complex refactoring and codebase exploration.
When to Choose Each
Choose Claude Code with LSP when:
- You prefer terminal-based workflows
- You need deep codebase analysis (impact assessment, architecture understanding)
- You're refactoring across multiple files with complex dependencies
- You want AI that can semantically navigate your code
Choose VS Code/Cursor when:
- You need the broadest language support
- You prefer visual interfaces for code review
- Your workflow centers on GUI-based development
Choose GitHub Copilot when:
- Your primary need is inline code suggestions
- You work mostly in the GitHub ecosystem
- You want minimal setup with existing IDE
Frequently Asked Questions
How much does Claude Code LSP cost?
Claude Code LSP is included in your existing Claude Code subscription or API usage at no additional cost. The LSP plugins themselves are open source and free. You only pay for Claude Code usage (API calls or subscription). For teams seeking cost-effective API access, laozhang.ai offers aggregated pricing starting at $5 with multi-model support—check the documentation at https://docs.laozhang.ai/ for current rates.
Can I create custom LSP plugins for unsupported languages?
Yes, Claude Code supports custom LSP plugins through the .lsp.json configuration format. You'll need to specify the language server command, file extensions, and optional settings. The official documentation at code.claude.com provides a complete reference for plugin creation, including transport configuration for stdio or TCP-based servers.
Does LSP work offline?
The LSP plugins and language servers run entirely locally—they don't require internet connectivity. However, Claude Code itself requires API access for the AI features, so you need internet for the conversational interface while LSP operations themselves are offline-capable.
How do I update LSP plugins?
Plugin updates depend on your marketplace configuration:
bash# Check for updates /plugin # Navigate to Marketplaces tab # Select your marketplace and enable auto-update # Manual update /plugin uninstall pyright@claude-code-lsps /plugin install pyright@claude-code-lsps
The official Anthropic marketplace auto-updates by default; third-party marketplaces may require manual refresh.
Can I use LSP with enterprise/team configurations?
Yes, add marketplace configuration to your project's .claude/settings.json for team-wide plugin availability. When collaborators trust the repository, Claude Code prompts them to install configured plugins automatically. See the plugins settings documentation for the enabledPlugins and extraKnownMarketplaces options.
What's the performance impact of enabling LSP?
LSP language servers consume memory proportional to project size. For typical projects under 100K lines of code, expect 200-500MB additional memory usage. Large monorepos may require more resources. The performance benefit (50ms vs 45 seconds for navigation) typically outweighs the memory cost for active development.
How does LSP work with multi-language projects?
Install plugins for each language in your project. Claude Code activates the appropriate language server based on file extensions. For example, a project with Python backend and TypeScript frontend would use both pyright and vtsls simultaneously, with Claude seamlessly switching context as you navigate between files.
Can I temporarily disable LSP?
Remove the environment variable or launch without it:
bash# Disable for a session ENABLE_LSP_TOOL=0 claude # Or simply launch without the variable claude # if not in your shell profile
Plugins remain installed but inactive without the environment variable.
Summary and Next Steps
Claude Code LSP transforms terminal-based AI coding assistance by adding semantic code understanding through the Language Server Protocol. The key points to remember:
Core Capabilities: Five LSP operations—goToDefinition, findReferences, hover, documentSymbol, and getDiagnostics—provide IDE-level code intelligence directly in your terminal conversations with Claude.
Broad Language Support: With 11 supported languages covering most mainstream development needs (Python, TypeScript, Go, Rust, Java, C/C++, C#, PHP, Kotlin, Ruby, HTML/CSS), you can leverage LSP regardless of your technology stack.
Dramatic Performance: The shift from text-based to semantic search delivers 900x performance improvements (50ms vs 45 seconds), enabling real-time code exploration during development conversations.
Straightforward Setup: Enable with one environment variable, add a marketplace, and install plugins—most developers complete setup in under five minutes.
Recommended Next Steps
If you're new to Claude Code, start with our free trial guide to understand the baseline capabilities before adding LSP.
For those already using Claude Code:
- Enable LSP for your primary language first
- Verify with the test commands in the verification section
- Gradually add plugins for secondary languages in your projects
- Explore the combined power of LSP navigation with Claude's reasoning
The combination of semantic code understanding with AI-powered analysis creates workflows impossible with either technology alone. Whether you're exploring an unfamiliar codebase, planning a major refactoring, or debugging complex type errors, Claude Code with LSP provides the foundation for more effective AI-assisted development.