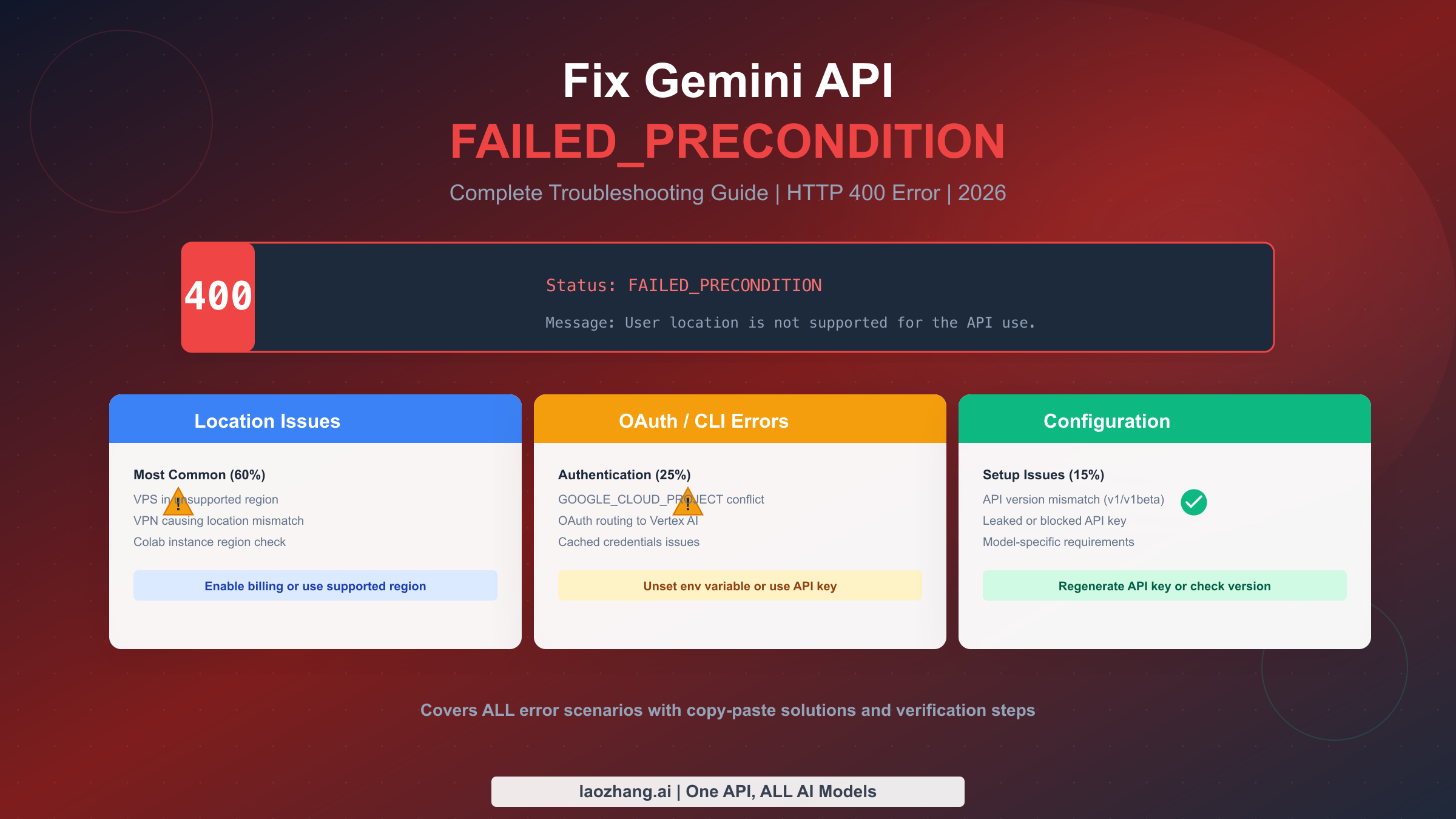
Getting the HTTP 400 FAILED_PRECONDITION error when calling the Gemini API stops your development cold. The error message might say "User location is not supported for the API use" or simply "Precondition check failed"—either way, your API calls fail and your project stalls. This guide provides the complete diagnostic and fix process for all FAILED_PRECONDITION variants, based on verified solutions from Google's official documentation and developer community experiences as of January 2026.
Understanding the FAILED_PRECONDITION Error
The FAILED_PRECONDITION error from the Gemini API indicates that a required condition for your API request was not met before the request was processed. Unlike authentication errors (401) or rate limiting errors (429), this error occurs during the pre-validation phase, meaning Google's servers reject the request before processing begins. Understanding which variant you're encountering is the first step toward a quick fix.
The three main error variants you'll encounter are fundamentally different problems requiring different solutions. The location-based error appears when your request originates from a region where the Gemini API free tier is unavailable. The OAuth/CLI error occurs specifically when using Google's Gemini CLI tool with OAuth authentication and a conflicting environment configuration. The configuration error happens when your API setup doesn't meet the requirements for the specific model or feature you're trying to access.
The error response typically follows this JSON structure, which helps identify the root cause:
json{ "error": { "code": 400, "message": "User location is not supported for the API use.", "status": "FAILED_PRECONDITION" } }
When you see "User location is not supported," you're dealing with the most common variant—geographic restrictions. When the message is simply "Precondition check failed" without location context, you're likely facing an OAuth routing issue or configuration mismatch. The Gemini Live session variant shows "Gemini Live session closed: Precondition check failed" and relates specifically to real-time audio features.
Each error type has a distinct fix path, so correctly identifying your error before attempting solutions saves significant debugging time. The following diagnostic flowchart helps you quickly determine which fix applies to your situation.
Quick Diagnostic Flowchart
Before diving into specific solutions, use this decision tree to identify your exact problem in under 30 seconds. Your error message text directly indicates which troubleshooting path to follow.
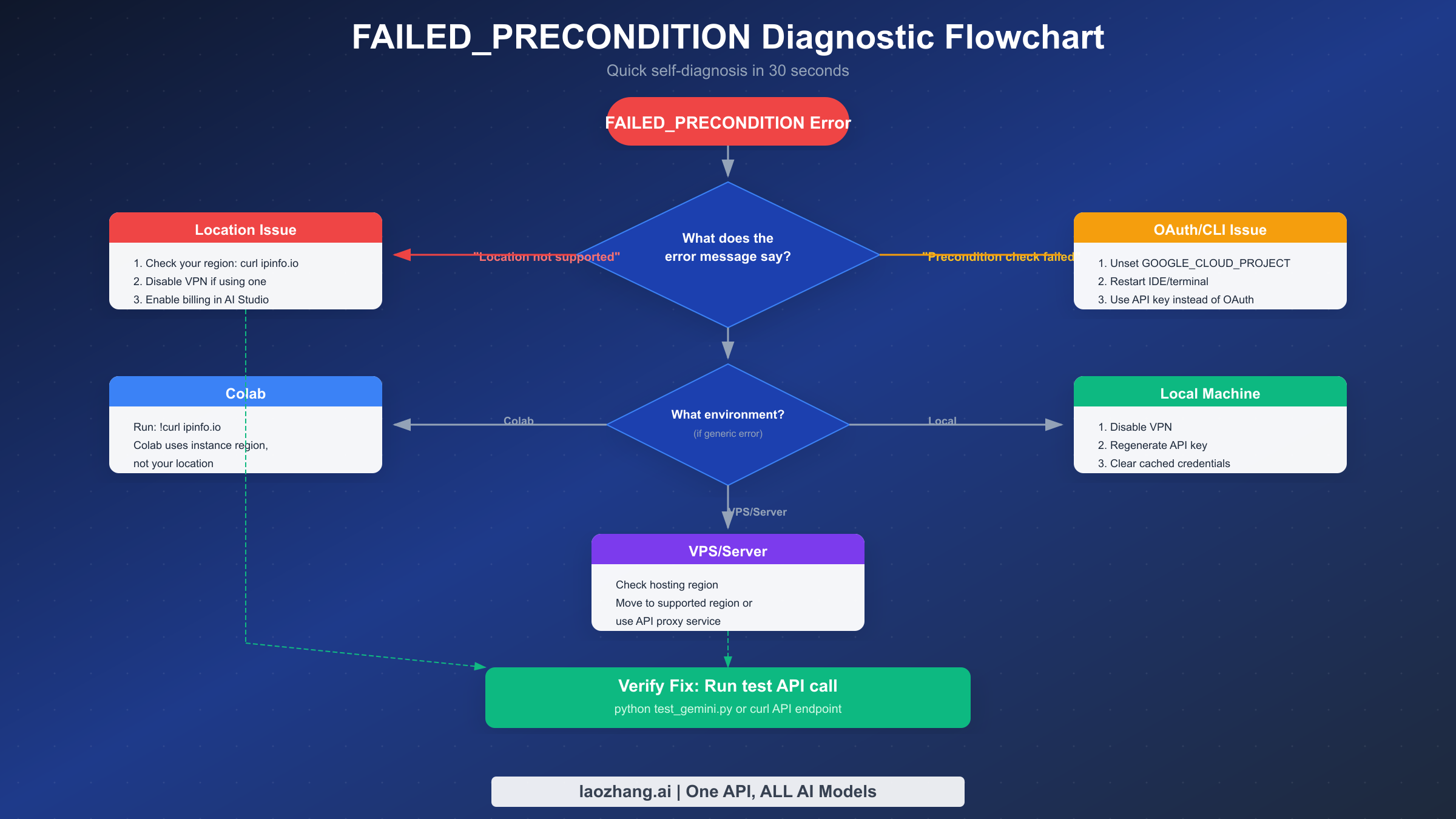
Start with the error message text. If it contains "location not supported," proceed to the location-based fixes in the next section. If it says "Precondition check failed" without location context and you're using Gemini CLI with OAuth, jump to the OAuth/CLI section. For generic errors without clear indicators, check your environment first—Colab users face different constraints than VPS or local development environments.
The quick reference table below maps common scenarios to their most likely causes:
| Your Situation | Most Likely Cause | First Step |
|---|---|---|
| VPS hosting (Hetzner, OVH, etc.) | Server region unsupported | Check server IP location |
| Working locally with VPN | VPN routing through blocked region | Disable VPN and retry |
| Gemini CLI after OAuth login | GOOGLE_CLOUD_PROJECT env conflict | Check environment variables |
| Google Colab notebook | Colab instance region | Run !curl ipinfo.io |
| Was working, suddenly failed | Region policy change or key issue | Generate new API key |
| Using v1beta features | API version mismatch | Verify endpoint URL |
The diagnostic takes 30 seconds; the wrong fix takes 30 minutes. Taking a moment to correctly identify your error type before attempting solutions dramatically reduces troubleshooting time.
Fixing Location-Based Errors
Location-based FAILED_PRECONDITION errors account for approximately 60% of all cases, making them the most common issue developers face. The error occurs because Google's Gemini API free tier has geographic restrictions—the service is available in 190+ countries, but the free tier specifically may be unavailable in certain regions or when accessing from certain hosting providers.
The core issue is where your request originates, not where you are physically located. If you're running code on a VPS hosted in Germany, your request originates from Germany regardless of whether you're sitting in San Francisco. This distinction trips up many developers who assume their personal location determines API access.
For developers running on cloud VPS providers, the first diagnostic step is confirming your server's actual location:
bashcurl ipinfo.io # Expected output shows your server's region { "ip": "xxx.xxx.xxx.xxx", "city": "Falkenstein", "region": "Saxony", "country": "DE", ... }
If your server is in a region where the free tier is restricted, you have three main options. The first and most reliable solution is enabling billing on your Google AI Studio account, which removes geographic restrictions for the paid tier. Navigate to Google AI Studio, access your account settings, and add a payment method. This doesn't mean you'll necessarily incur charges—the paid tier still includes substantial free quotas—but it removes the regional lockout.
The second option is deploying your application from a supported region. Cloud providers like AWS, GCP, and Azure allow you to select specific regions. US-based regions consistently work well with the Gemini API free tier. If you're using a VPS provider like Hetzner or OVH that primarily serves European regions, consider migrating to a US-based provider or using a cloud function deployed in a US region as a proxy.
For local development issues related to VPN usage, the solution is straightforward:
bash# Disable VPN temporarily # Then verify your actual IP curl ipinfo.io # Generate a fresh API key after disabling VPN # Old keys may have been flagged based on VPN location
Generating a new API key after fixing the location issue is often necessary because Google may have flagged your existing key based on suspicious location patterns. A developer who traveled internationally while using VPN, then returned home, might find their original key permanently associated with the problematic location data. Creating a fresh key from your actual location resolves this.
For Google Colab users, the situation requires understanding that Colab instances run on Google's infrastructure, and the instance location—not your browser location—determines API access. Check the instance region with:
python!curl ipinfo.io
If the Colab instance is in a restricted region, you have limited options since you cannot control Colab's infrastructure. The practical solution for Colab users facing location restrictions is to enable billing on your Google account, which removes the regional limitations regardless of where the Colab instance runs.
Billing and Regional Restrictions
Understanding when billing is actually required versus when it's optional helps you make informed decisions about your Gemini API setup. The confusion around billing requirements stems from Google's tiered access model, where free tier availability varies by region while paid tier access is globally available.
The Gemini API free tier is available in 190+ countries and territories according to Google's official documentation as of January 2026. However, "available" means the service can function—it doesn't mean the free tier specifically is accessible from all locations. Some hosting providers' IP ranges may be excluded even in supported countries, and VPN traffic may route through restricted regions.
The billing requirements break down as follows:
| Access Type | Billing Required | Geographic Restrictions |
|---|---|---|
| Free tier, supported region | No | Limited to 190+ countries |
| Free tier, VPS in EU | Often yes | Many EU hosting IPs restricted |
| Paid tier, any region | Yes | None |
| Vertex AI access | Yes | Project-based |
Enabling billing doesn't automatically incur charges. Google's pricing structure includes generous free quotas within the paid tier—you only pay when exceeding these quotas. The Gemini API pricing model charges per million input/output tokens, with rates varying by model. For most development and testing scenarios, you'll remain well within free quota limits even with billing enabled.
To enable billing in Google AI Studio:
- Navigate to Google AI Studio
- Click on your account settings (profile icon)
- Select "Billing" from the menu
- Add a payment method (credit card or Google Pay)
- Generate a new API key after billing is enabled
After enabling billing, generate a fresh API key rather than reusing your existing key. The new key will be associated with your billing-enabled account status from creation, avoiding any lingering issues from the previous free-tier key.
For developers concerned about unexpected charges, Google Cloud Console allows setting up budget alerts and spending limits. You can configure notifications at specific spending thresholds and even set hard caps that disable API access if exceeded. This provides peace of mind when enabling billing for development purposes.
If you need API access without enabling billing—perhaps for a student project or personal experimentation—consider using managed API services like laozhang.ai that handle billing complexity while providing competitive pricing and removing regional restrictions.
OAuth and CLI Authentication Errors
The "Precondition check failed" error appearing specifically during Gemini CLI usage with OAuth authentication stems from a well-documented environment variable conflict. This issue affects developers who have GOOGLE_CLOUD_PROJECT set in their environment, typically from previous Google Cloud SDK work.
The root cause is OAuth credential routing confusion. When Gemini CLI attempts OAuth authentication, the presence of GOOGLE_CLOUD_PROJECT causes the authentication library to route the request through Vertex AI endpoints (enterprise) rather than the personal Gemini API endpoints. Since your personal OAuth credentials aren't valid for Vertex AI project authentication, the precondition check fails.
The fix is straightforward—remove the conflicting environment variable:
bash# Check if the variable is set echo $GOOGLE_CLOUD_PROJECT # If it returns a value, unset it unset GOOGLE_CLOUD_PROJECT # For persistent removal, check your shell profile # Remove or comment out any GOOGLE_CLOUD_PROJECT export in: # ~/.bashrc, ~/.zshrc, or ~/.profile # Restart your terminal or source your profile source ~/.zshrc # or ~/.bashrc
For VS Code users, the environment can persist in unexpected ways. The solution requires not just unsetting the variable but restarting VS Code completely:
bash# Close VS Code entirely # Then in terminal: unset GOOGLE_CLOUD_PROJECT # Relaunch VS Code from terminal to inherit clean environment code .
If you need GOOGLE_CLOUD_PROJECT for other work, you have several options. The cleanest approach is using different terminals or shell sessions for different projects—one with the variable set for Google Cloud work, another without for Gemini CLI. Alternatively, you can temporarily set the variable only when needed:
bash# Run your GCP commands with the variable set inline GOOGLE_CLOUD_PROJECT=my-project gcloud ... # Gemini CLI runs without the variable in the global environment gemini chat "Hello"
An alternative to OAuth authentication that avoids this issue entirely is using API key authentication instead. Generate an API key from Google AI Studio and configure Gemini CLI to use it:
bash# Set API key authentication export GEMINI_API_KEY=your-api-key-here # Or configure in Gemini CLI settings gemini config set api_key your-api-key-here
API key authentication bypasses the OAuth routing issue completely because it doesn't involve the authentication library's project detection logic. For personal development use, API keys are often simpler and equally secure when properly managed.
For enterprise users who specifically need Vertex AI access through Gemini CLI, configure the CLI to use Vertex AI authentication explicitly:
bash# Configure for Vertex AI gemini config set auth_type vertex-ai gemini config set project your-project-id gemini config set location us-central1
This explicit configuration ensures the CLI routes through Vertex AI intentionally rather than accidentally due to environment variable detection.
Configuration and API Version Issues
Beyond location and authentication issues, FAILED_PRECONDITION errors can stem from API configuration mismatches. These typically involve using the wrong API version for a feature, model-specific requirements not being met, or API key issues.
API version selection matters for accessing certain features. The Gemini API exposes two primary versions: v1 (stable) and v1beta (preview features). Some newer capabilities are only available in v1beta, while v1 guarantees stability but may lack cutting-edge features. Using the wrong version for your intended feature triggers a precondition failure.
pythonimport google.generativeai as genai # For stable features, use v1 (default) genai.configure(api_key="YOUR_API_KEY") # For preview features, explicitly specify v1beta # Check the feature documentation for version requirements
Verify your endpoint URLs match your intended API version:
# v1 stable endpoint
https://generativelanguage.googleapis.com/v1/models/gemini-pro:generateContent
# v1beta preview endpoint
https://generativelanguage.googleapis.com/v1beta/models/gemini-2.0-flash:generateContent
Model availability varies between versions. The Gemini 2.5 models with thinking capabilities enabled by default (as of January 2026) may have different availability in v1 versus v1beta. Always check the Gemini API documentation for current model availability and version requirements.
API key issues can also trigger FAILED_PRECONDITION errors when Google detects potentially leaked or suspicious key usage. If your key appeared in public repositories, logs, or was used from many different locations rapidly, Google may restrict it:
bash# Generate a new API key from Google AI Studio # https://aistudio.google.com/app/apikey # Update your environment export GEMINI_API_KEY=new-api-key-here # Or update your configuration files # .env file: GEMINI_API_KEY=new-api-key-here
When managing API keys, follow these best practices to avoid precondition failures related to key security:
- Never commit API keys to version control
- Use environment variables or secret management services
- Rotate keys periodically, especially after any potential exposure
- Use separate keys for development and production environments
If you've verified your API version is correct and your key is fresh but still see precondition errors, check for 401 authentication errors which can sometimes manifest with similar symptoms but require different fixes.
Verification and Testing
After applying a fix, verifying that your changes actually resolved the issue prevents wasted time on incorrect solutions. A quick test script confirms your Gemini API access works before you continue development.
The minimal verification test takes under 30 seconds:
pythonimport google.generativeai as genai import os # Configure with your API key api_key = os.environ.get('GEMINI_API_KEY') if not api_key: print("Error: GEMINI_API_KEY environment variable not set") exit(1) genai.configure(api_key=api_key) # Simple test request try: model = genai.GenerativeModel('gemini-2.0-flash') response = model.generate_content("Say 'API connection successful' in exactly those words.") print(f"Success: {response.text}") except Exception as e: print(f"Error: {e}")
Run this script after each fix attempt. A successful response confirms the FAILED_PRECONDITION error is resolved. If you still see errors, you may have a different issue than initially diagnosed—return to the diagnostic flowchart.
For command-line verification without Python:
bash# Using curl to test API access directly curl -X POST \ "https://generativelanguage.googleapis.com/v1/models/gemini-2.0-flash:generateContent?key=$GEMINI_API_KEY" \ -H "Content-Type: application/json" \ -d '{"contents":[{"parts":[{"text":"Say hello"}]}]}' # Successful response includes generated content # Error response shows the error message and status
Common issues after applying fixes include cached credentials and environment persistence. If your fix doesn't seem to take effect:
- Restart your terminal/IDE completely
- Verify the environment variable is actually unset:
echo $GOOGLE_CLOUD_PROJECT - Generate a fresh API key if you changed billing or location
- Clear any cached authentication tokens:
rm -rf ~/.cache/google-*
For automated testing in CI/CD pipelines, include a Gemini API health check that runs before your main application tests:
yaml# GitHub Actions example - name: Verify Gemini API Access env: GEMINI_API_KEY: ${{ secrets.GEMINI_API_KEY }} run: | python verify_gemini.py
This catches configuration issues early in the deployment pipeline rather than discovering them in production.
Prevention Best Practices
Preventing FAILED_PRECONDITION errors is more efficient than troubleshooting them repeatedly. These practices help you set up Gemini API integrations that remain stable across environments and deployments.
For production deployments, always enable billing regardless of expected usage. The cost of occasional API calls is minimal compared to the debugging time when geographic restrictions cause unexpected failures. Production systems need reliability over cost optimization at the free tier level.
Environment variable management prevents OAuth routing conflicts. Structure your development environment to isolate Gemini API configuration from other Google Cloud settings:
bash# Use specific variable names for Gemini export GEMINI_API_KEY=your-key # Keep GOOGLE_CLOUD_PROJECT for GCP-specific work # But don't set it globally if you use Gemini CLI # Or use a project-specific .env file # .env.gemini GEMINI_API_KEY=your-key
Choose deployment regions intentionally. When setting up cloud infrastructure, select US-based regions for Gemini API workloads to avoid geographic restrictions:
| Provider | Recommended Region | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| AWS | us-east-1, us-west-2 | Lambda, EC2, ECS |
| GCP | us-central1, us-east1 | Cloud Functions, Cloud Run |
| Azure | eastus, westus2 | Functions, Container Apps |
| Vercel | iad1 (Washington DC) | Serverless Functions |
Implement proper error handling in your application code to distinguish between transient errors and configuration issues:
pythonimport google.generativeai as genai from google.api_core import exceptions def call_gemini(prompt: str) -> str: try: model = genai.GenerativeModel('gemini-2.0-flash') response = model.generate_content(prompt) return response.text except exceptions.FailedPrecondition as e: # Log and alert - this requires configuration fix logger.error(f"Gemini FAILED_PRECONDITION: {e}") raise ConfigurationError("Gemini API configuration issue") except exceptions.ResourceExhausted as e: # Rate limit - implement backoff logger.warning(f"Rate limited: {e}") raise RateLimitError("Retry with backoff")
For teams, document your Gemini API configuration in your project setup guide. Include the required environment variables, billing status, and region requirements so new team members don't encounter these errors during onboarding.
If you're experiencing 429 resource exhausted errors alongside precondition issues, you may need to address both rate limiting and configuration simultaneously.
Frequently Asked Questions
Why does Gemini API say my location is not supported even though I'm in the US?
Your physical location doesn't determine API access—your request's origin IP does. If you're using a VPN, your traffic routes through the VPN server's location. If you're running code on a cloud server, that server's location matters. Disable VPN and check your actual IP with curl ipinfo.io. If using a cloud provider, verify your deployment region is US-based.
Is the Gemini API free tier available in my country?
Google officially supports 190+ countries and territories, but free tier availability within those regions varies. The most reliable way to determine availability is attempting an API call from your region. If you receive a location error, enable billing to access the paid tier which has no geographic restrictions. Check Gemini's regional restrictions guide for detailed information.
How do I fix "Precondition check failed" in Gemini CLI?
This specific error in Gemini CLI typically indicates the GOOGLE_CLOUD_PROJECT environment variable is interfering with OAuth authentication. Run echo $GOOGLE_CLOUD_PROJECT—if it shows a value, run unset GOOGLE_CLOUD_PROJECT and restart your terminal. Alternatively, use API key authentication instead of OAuth by setting GEMINI_API_KEY in your environment.
Do I need to enable billing to use Gemini API?
Not necessarily—the free tier works in many regions without billing. However, enabling billing removes all geographic restrictions and provides access to higher quotas. Enabling billing doesn't mean you'll be charged; you only pay when exceeding the generous free quotas included in the paid tier.
Why did my working Gemini API suddenly fail with FAILED_PRECONDITION?
Several scenarios cause previously working setups to fail. Google periodically updates regional restrictions, potentially affecting previously allowed IP ranges. Your API key may have been flagged for suspicious activity if it was used from multiple locations. VPN software updates can change routing. The fix is usually generating a new API key after verifying your location setup is correct.
Can I use Gemini API with VPN enabled?
Technically yes, but it's unreliable. VPN routing can place your requests in restricted regions even if your physical location is supported. For development, disable VPN when using Gemini API. For production, deploy to a supported cloud region rather than relying on VPN routing.
What's the difference between v1 and v1beta API endpoints?
The v1 endpoint provides stable features with guaranteed compatibility. The v1beta endpoint offers preview features that may change. Some newer models and features require v1beta. Check your specific use case in the Gemini API documentation to determine which version you need. Using the wrong version for a feature triggers precondition errors.
How do I verify my Gemini API fix worked?
Run a minimal test request after applying any fix. The Python script in the Verification section provides a quick check. A successful response confirms the fix. If errors persist, you may have misdiagnosed the issue—return to the diagnostic flowchart to verify you're addressing the correct problem.
The FAILED_PRECONDITION error, while frustrating, has well-documented causes and fixes. Location issues resolve with billing enablement or region changes. OAuth conflicts fix with environment variable cleanup. Configuration problems clear up with version verification and fresh API keys. Use the diagnostic flowchart to identify your specific issue, apply the targeted fix, and verify with a test request. Most developers resolve this error within 10 minutes using the correct approach.
For ongoing API management and to avoid regional restrictions entirely, consider using API aggregation services like laozhang.ai that provide unified access to multiple AI models including Gemini, with consistent availability and simplified billing.