OpenClaw troubleshooting starts with one command: openclaw status --all. This comprehensive guide covers every error code from 401 authentication failures to the notorious "invalid beta flag" with Bedrock and Vertex AI. Whether you're facing rate limits (429), gateway issues (502), or configuration problems, you'll find step-by-step fixes with copy-paste commands that work immediately. The guide includes automated diagnostic scripts, platform-specific solutions for macOS, Linux, and Windows, plus prevention strategies to keep your OpenClaw installation running smoothly.
TL;DR
Run openclaw status --all first to get a complete diagnostic report. For quick fixes: 401 errors need openclaw models auth setup-token, 429 rate limits require waiting 60 seconds or adding fallback models, invalid beta flag is solved by switching to direct Anthropic API or disabling beta features. When in doubt, openclaw doctor --fix auto-repairs most configuration issues. Keep reading for detailed solutions to 30+ error types.
Quick Start: Diagnose Your Error in 60 Seconds
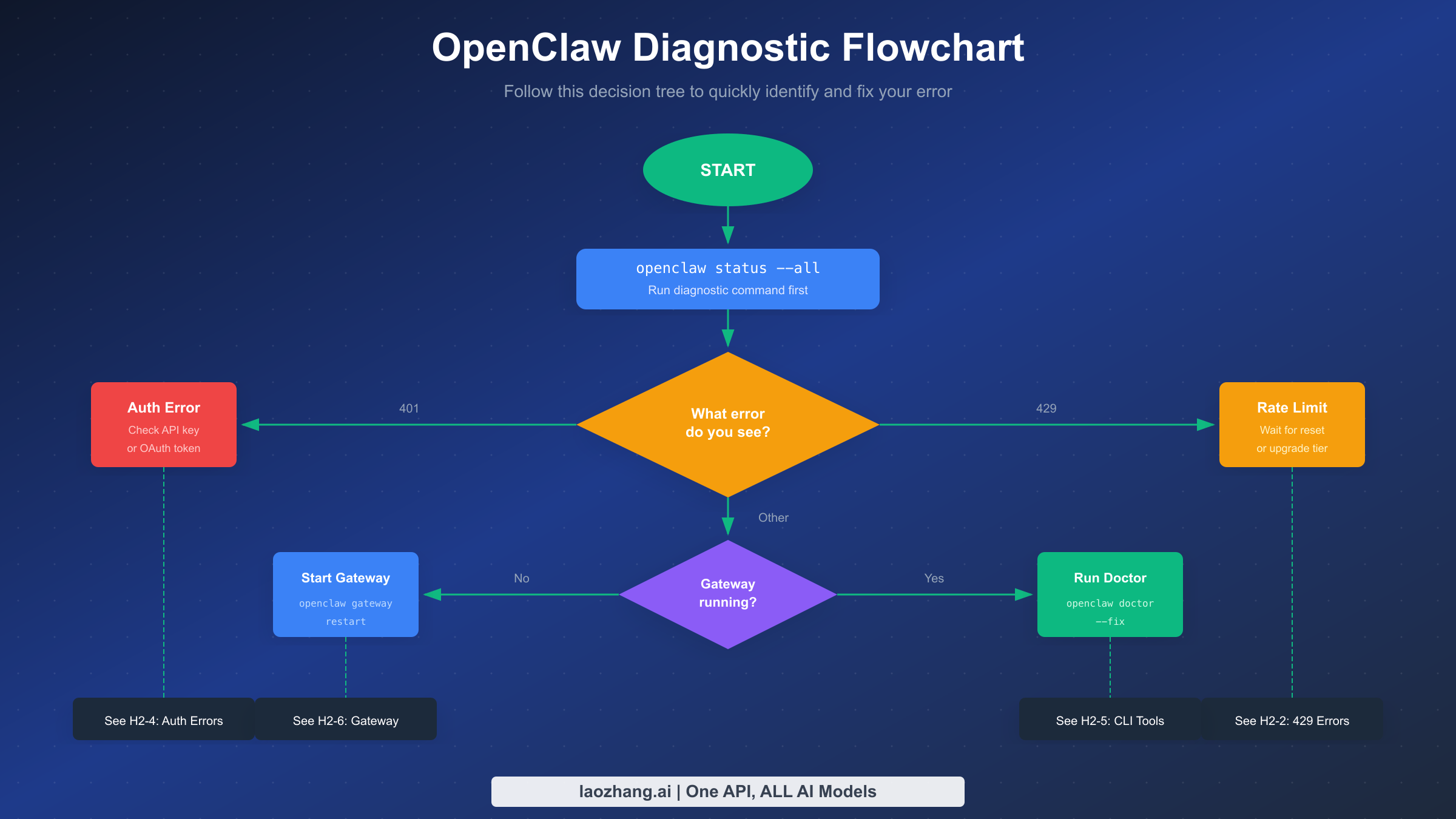
When OpenClaw stops working, your first instinct might be to search for the specific error message. That approach works, but there's a faster path to resolution. OpenClaw includes powerful diagnostic tools that can identify the root cause within seconds. The key is knowing which command to run based on what you're experiencing.
Start with the universal diagnostic command that reveals everything about your OpenClaw installation. Running openclaw status --all produces a comprehensive report covering your operating system configuration, gateway status, authentication state, and provider connectivity. This single command often reveals the exact problem without any guesswork. The output is designed to be human-readable while also redacting sensitive information like API tokens, so you can safely share it when seeking help.
If the status command shows the gateway is running but you're still experiencing issues, escalate to openclaw status --deep. This variant performs actual connectivity tests against your configured providers, verifying that API calls can reach their destinations. Network issues, firewall blocks, and provider outages all become visible through this deeper probe.
For problems that appear intermittently or only under certain conditions, openclaw logs --follow streams live log output to your terminal. Watch this stream while reproducing the issue to capture the exact error context. Press Ctrl+C when you've gathered enough information. The combination of status reports and live logs provides complete visibility into what's happening inside your OpenClaw installation.
The first 60 seconds of troubleshooting should follow this pattern: status report, then deeper probe if needed, then live logs for runtime issues. This systematic approach catches 90% of problems before you need to dive into specific error code documentation. When you do need specific solutions, the following sections provide detailed fixes for every common error type.
HTTP Error Codes Reference
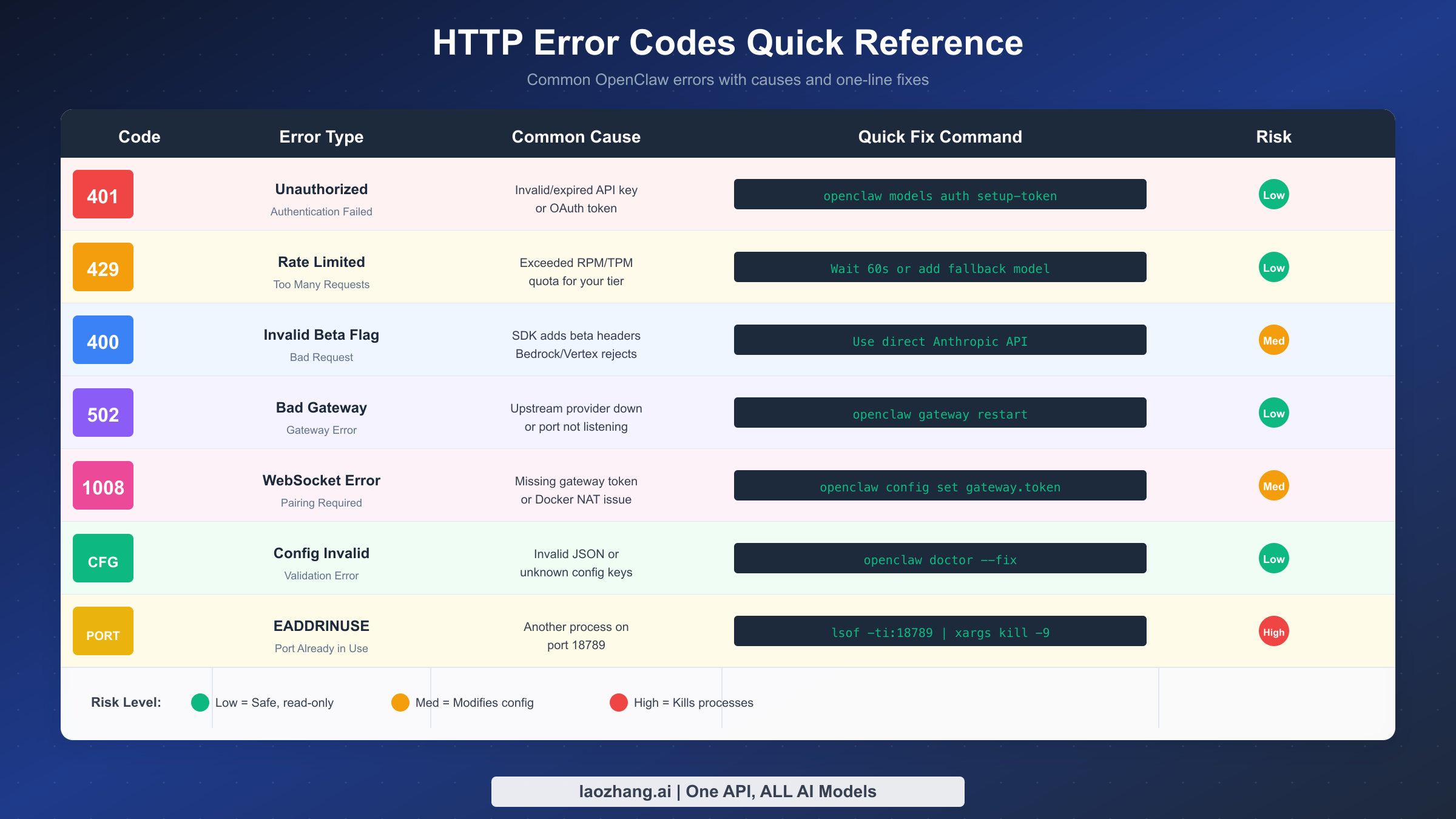
HTTP error codes tell you exactly what went wrong during an API request. Understanding these codes transforms cryptic failures into actionable diagnoses. OpenClaw surfaces these errors from multiple sources: your local gateway, the AI providers you've configured, and occasionally intermediate proxies. Each source produces slightly different error patterns, but the fix approach remains consistent.
The 401 Unauthorized error appears when authentication fails at any point in the request chain. Within OpenClaw's architecture, this typically means your API key has expired, your OAuth token needs refreshing, or credentials are missing entirely for a specific provider. The diagnostic command openclaw models status reveals which providers lack valid credentials. When you see "No API key found for provider anthropic" or similar messages, the fix involves re-authenticating that specific provider.
For Anthropic specifically, you have two authentication options. If you're using OAuth tokens (typically set up during initial onboarding), these can expire and require refresh. Running /logout followed by /login in your chat interface triggers a new OAuth flow. Alternatively, switch to the more reliable setup-token approach with openclaw models auth setup-token --provider anthropic. This method uses long-lived API keys that don't require periodic refresh.
The 429 Too Many Requests error indicates you've exceeded rate limits. Anthropic structures limits by usage tier, with Tier 1 allowing 50 requests per minute and higher tiers scaling up to 4,000 RPM (Anthropic official documentation, 2026-02-04). When you hit these limits, the API returns a retry-after header indicating how long to wait. OpenClaw should handle this automatically with exponential backoff, but a known bug (GitHub issue #5159) sometimes causes aggressive retry loops that hammer the API.
The practical fix for rate limiting involves multiple strategies. First, wait for the retry window, typically 60 seconds for most providers. Second, configure fallback models so OpenClaw can switch providers when one is rate-limited. Third, consider upgrading your API tier if you consistently hit limits. For users consuming high volumes, API proxy services can provide higher quotas and more stable connections through aggregated capacity.
The 400 Bad Request error covers many situations, but the most notorious is the "invalid beta flag" error. This occurs specifically when using Claude through AWS Bedrock or Google Vertex AI rather than direct Anthropic API access. The Claude SDK automatically attaches experimental feature headers that these managed services don't recognize. The next section dives deep into fixing this particular error.
Gateway errors like 502 Bad Gateway typically indicate the upstream AI provider is temporarily unavailable. These resolve themselves within minutes in most cases. If a 502 persists, check provider status pages and ensure your gateway can reach the internet. Running openclaw gateway probe tests network connectivity specifically for the gateway component. For users behind corporate firewalls, proxy configuration may be necessary. Set the HTTP_PROXY and HTTPS_PROXY environment variables in your shell or in the ~/.openclaw/.env file to route requests through your corporate proxy.
The WebSocket error 1008 deserves special mention because it appears frequently in Docker deployments and remote access scenarios. This error message, typically reading "disconnected (1008): unauthorized: gateway token missing" or "pairing required", indicates that the browser cannot authenticate with the gateway. The root cause differs between deployment types. In Docker, NAT networking prevents direct WebSocket connections, requiring explicit token configuration. In remote access scenarios, the gateway expects authentication but hasn't been configured with a token. The fix for both cases involves setting openclaw config set gateway.token <your-secure-token> on the gateway host, then providing that same token when connecting from the client.
Port conflicts produce EADDRINUSE errors that prevent the gateway from starting. When you see "address already in use :::18789", another process already occupies the default gateway port. Diagnostic steps vary by platform. On macOS and Linux, lsof -i :18789 identifies the conflicting process. On Windows, netstat -ano | findstr :18789 provides similar information. Once identified, you can either stop the conflicting process or change OpenClaw's port with openclaw config set gateway.port 18790 (or another available port). Remember that changing the port requires updating any clients configured to connect to the old port number.
Configuration validation errors manifest as "Gateway won't start - configuration invalid" messages accompanied by detailed Zod validation output. These errors occur when your openclaw.json file contains invalid JSON syntax, unknown configuration keys, or values that don't match expected types. Common causes include manually editing the configuration file and introducing typos, copying configuration from older versions that use deprecated key names, and partial updates that leave configuration in an inconsistent state. The openclaw doctor command identifies specific validation failures and their locations in the configuration file. Running openclaw doctor --fix applies automatic migrations and corrections for known issues, while more unusual problems require manual editing of the configuration file.
The Invalid Beta Flag Error Explained
The "invalid beta flag" error deserves its own section because it affects a specific but growing user population: those running Claude through AWS Bedrock or Google Vertex AI. When you encounter ValidationException: invalid beta flag or 400 Bad Request: invalid beta flag, your AI assistant becomes completely unresponsive, and messaging platforms show blank responses.
Understanding why this happens requires knowing how Claude's SDK works. Anthropic's official SDK automatically attaches beta headers to API requests, enabling experimental features like prompt caching and extended tool use. These headers, such as anthropic-beta: claude-code-20250219, work perfectly with the direct Anthropic API. However, AWS Bedrock and Google Vertex AI, as managed services, only support the stable Claude API surface. They actively reject any request containing beta headers.
The frustrating aspect is that you might not have explicitly enabled any beta features. OpenClaw or its underlying libraries can add these headers automatically, causing failures that seem to come from nowhere. The error cascades because fallback models often encounter the same beta header issue.
Five solutions exist, ranked from simplest to most comprehensive. The first approach modifies your OpenClaw configuration to disable beta features entirely. Add "beta_features": [] to your agent configuration, which prevents the SDK from attaching any experimental headers. This works immediately but limits you to stable features only.
The second and most reliable solution switches to the direct Anthropic API endpoint. If you don't specifically need Bedrock or Vertex AI for compliance or regional reasons, direct API access avoids the header compatibility problem entirely. Update your model configuration to use anthropic as the provider rather than bedrock or vertex.
The third approach uses LiteLLM as an intermediary proxy with header filtering enabled. Configure litellm.drop_params = True in your LiteLLM settings, which strips unrecognized parameters before forwarding requests to Bedrock or Vertex. This preserves your cloud provider choice while solving compatibility issues.
The fourth solution specifically targets prompt caching, which is a common source of beta headers. Set "cache": {"enabled": false} in your configuration as a temporary workaround. You lose caching performance benefits but regain functionality.
The fifth approach adopts an OpenAI-compatible interface through proxy services. Platforms like laozhang.ai provide unified API access that handles provider differences internally. You use a standardized interface while the service manages beta header compatibility across different backends. This approach also solves rate limiting issues by aggregating capacity across providers.
Authentication Errors Deep Dive
Authentication in OpenClaw operates through a three-layer system, and understanding this architecture helps diagnose which layer is failing. The first layer is your local configuration, stored in ~/.openclaw/openclaw.json and the agent-specific auth-profiles.json files. The second layer is the OpenClaw gateway, which validates credentials and manages connections to upstream providers. The third layer is the upstream providers themselves: Anthropic, OpenAI, OpenRouter, and others.
When authentication fails, the error message often indicates which layer is involved. "No API key found for provider" points to the local configuration layer, typically missing or corrupted auth-profiles. "OAuth token refresh failed" indicates the gateway layer encountered issues renewing credentials with the upstream provider. "Invalid API key" from the provider response means the credentials reached the provider but were rejected.
Diagnosing the correct layer prevents wasted troubleshooting effort. Run openclaw status first, which performs read-only checks without modifying anything. The output shows your authentication state for each configured provider. Follow up with openclaw models status to verify credential availability. If issues appear, openclaw doctor performs comprehensive validation and reports specific problems.
For OAuth-related failures, the fix depends on your setup. Browser-based OAuth flows can be re-triggered with /logout and /login commands in your chat interface. However, for headless environments without browser access, setup-tokens provide a more robust alternative. Generate a setup token through the provider's web interface, then run openclaw models auth paste-token --provider anthropic to configure it.
API key issues require verification at the provider level. Check that your key hasn't been revoked, hasn't exceeded its expiration date, and has sufficient billing credits associated with it. For Anthropic specifically, you must add a credit card and pre-load at least $5 to use the API via code, even if the web chat is free (Anthropic official documentation, 2026-02-04). Trial credits eventually expire, causing sudden authentication failures.
Platform-specific authentication issues also deserve attention. On macOS, Keychain access permissions can block credential retrieval silently. On Linux, file permissions on the .openclaw directory may prevent reading auth profiles. On Windows, environment variable conflicts between system and user scopes cause credential confusion. Each platform section in the installation guide covers these scenarios.
When migrating from ClawdBot (the previous name for OpenClaw), legacy credential formats may persist and cause authentication errors. Running openclaw doctor --fix includes migration logic that updates old credential formats to the current schema. This automatic migration handles most transition issues, though you may need to re-authenticate providers that used the old format.
Multi-agent setups introduce additional authentication complexity. Each agent in OpenClaw can have its own authentication profile, stored in separate auth-profiles.json files within agent-specific directories. When authentication works for one agent but fails for another, the issue likely lies in per-agent credential configuration rather than global settings. Copy the working auth-profiles.json to the failing agent's directory, or run the authentication flow specifically for that agent using openclaw models auth <provider> --agent <agent-id>. This isolation allows different agents to use different credentials or even different providers.
Rate limit management ties directly into authentication tiers. Your authentication determines which tier you occupy, which in turn sets your rate limits. Anthropic's tier system starts at Tier 1 with $5 credit purchase, offering 50 RPM and 30,000 input tokens per minute for Claude Sonnet 4.x models. Tier 2 at $40 expands to 1,000 RPM and 450,000 ITPM. Tier 3 at $200 provides 2,000 RPM and 800,000 ITPM. Tier 4 at $400 reaches 4,000 RPM and 2,000,000 ITPM. Understanding your tier helps predict when you'll hit rate limits and whether upgrading makes financial sense for your usage patterns. The Claude Console shows your current tier and usage statistics, enabling informed decisions about tier advancement.
Session management errors often masquerade as authentication issues. When OpenClaw reports "session expired" or "session not found", the problem may not be authentication at all. Sessions have configurable idle timeouts, reset triggers, and history limits. Check session.reset.idleMinutes in your configuration, which defaults to values that may not match your usage patterns. Extending this value prevents unexpected session terminations during long work periods. Similarly, session.historyLimit controls how many messages the session retains before truncating, which can cause context loss that appears as authentication or model failures.
Master the OpenClaw CLI Diagnostic Tools

The OpenClaw command-line interface includes a comprehensive toolkit for diagnosing and repairing problems. Mastering these commands transforms you from someone who searches for error messages into someone who systematically identifies and resolves issues. Each command serves a specific purpose, and knowing when to use each one accelerates your troubleshooting workflow.
The openclaw status family of commands forms your first line of diagnostics. The base command provides a quick local overview covering operating system details, gateway state, authentication status, and provider configuration. Adding --all extends this with a log tail section showing recent activity, while --deep performs actual connectivity probes against configured providers. Always start with status commands because they're completely safe and read-only.
The openclaw doctor command validates your entire configuration against the expected schema. It catches invalid JSON syntax, unknown configuration keys, type mismatches, and legacy keys that need migration. Think of it as a configuration linter that reports every deviation from the expected format. When combined with the --fix flag, doctor attempts automatic repairs for common issues like permission problems, missing directories, and outdated configuration formats.
Gateway management commands control the background service that handles all OpenClaw communications. openclaw gateway status shows whether the gateway is running, its process ID, and any recent errors. openclaw gateway restart stops and restarts the service, which resolves many transient issues. For more serious problems, openclaw gateway install --force reinstalls the gateway service configuration, useful when CLI and service configs have drifted out of sync.
Model and authentication commands manage your API credentials. openclaw models status displays credential availability for each provider. openclaw models list shows all available models with their IDs and aliases. openclaw models auth <provider> initiates authentication flows for specific providers. These commands are essential when 401 errors indicate missing or invalid credentials.
Log access commands help diagnose runtime issues that don't appear in status reports. openclaw logs --follow streams live logs, perfect for watching what happens when you trigger an error. Logs include timestamps, severity levels, and detailed context about each operation. For post-mortem analysis, log files persist at /tmp/openclaw/openclaw-YYYY-MM-DD.log or your configured logging location.
Channel-specific commands diagnose issues with messaging platforms like WhatsApp, Telegram, and Discord. openclaw channels status shows connection state for each configured channel. Adding --probe performs connectivity tests that verify not just configuration but actual message flow capability.
The configuration command family lets you modify settings without directly editing JSON files. openclaw config get <key> reads specific configuration values, useful for verifying current settings. openclaw config set <key> <value> writes new values, handling JSON formatting automatically. For complex nested values, use dot notation like openclaw config set agents.defaults.model.primary claude-sonnet-4-5. These commands provide safer configuration changes than manual JSON editing, with built-in validation that catches errors before they corrupt your configuration file.
Understanding command output interpretation accelerates troubleshooting significantly. Status commands use consistent formatting: green checkmarks indicate healthy components, yellow warnings suggest non-critical issues worth monitoring, and red errors identify problems requiring immediate attention. The verbose flag (-v or --verbose) on most commands increases output detail, revealing internal decision-making that helps diagnose subtle issues. When sharing diagnostic output for support requests, include verbose output to give helpers maximum context about your situation.
Installation and Configuration Errors
Installation failures represent a special category of errors because they prevent OpenClaw from running at all. These errors have platform-specific causes and solutions, making generic troubleshooting advice less useful. Understanding the installation requirements for your specific platform prevents most of these issues before they occur.
Node.js version mismatches cause the most common installation failures. OpenClaw requires Node.js version 22 or later, and attempting installation with older versions produces immediate errors. Verify your version with node --version before proceeding. If you're using a version manager like nvm or fnm, ensure you've activated the correct Node version in your current shell session.
The sharp native module dependency causes installation failures when system build tools are missing. On macOS, running xcode-select --install installs the command-line tools needed for native module compilation. On Linux, apt install build-essential python3 or the equivalent for your distribution provides the necessary compilers. On Windows, the recommended approach uses WSL2 rather than native Windows, as documented in the OpenClaw installation guide.
Path configuration issues manifest as "openclaw: command not found" errors after seemingly successful installation. The npm global bin directory must be on your system PATH. For bash and zsh on macOS and Linux, add export PATH="$(npm prefix -g)/bin:$PATH" to your shell configuration file. On Windows, ensure %AppData%\npm appears in your PATH environment variable.
Permission errors during installation often tempt users to run sudo npm install -g, but this creates worse problems down the line. Instead, fix the npm directory ownership with sudo chown -R $USER:$(id -gn $USER) ~/.npm and retry without sudo. Using a Node version manager automatically handles permissions correctly.
Configuration validation errors prevent the gateway from starting even after successful installation. These appear as "Gateway configuration invalid" messages with Zod validation details. Common causes include invalid enum values (like gateway.bind: "invalid" instead of valid options like loopback, lan, or tailnet), type mismatches (string where number expected), and leftover keys from older configuration schemas.
The openclaw doctor command catches these configuration issues and reports exactly what needs fixing. Running openclaw doctor --fix attempts automatic repair, migrating legacy keys and correcting common mistakes. For manual repair, the configuration file lives at ~/.openclaw/openclaw.json and follows a documented JSON schema.
Docker installations face a specific "pairing required" (error 1008) issue due to NAT networking. When accessing the WebUI through Docker, the browser cannot establish the expected direct connection. The fix involves either using localhost:18789 for local access or configuring proper token authentication for remote access with openclaw config set gateway.token <value>.
Headless server installations present unique challenges because they lack graphical interfaces for OAuth flows and browser-based authentication. The --headless flag on the onboarding command adapts the setup process for non-graphical environments. For authentication specifically, setup-tokens provide a headless-friendly alternative to OAuth. Generate the token on any device with a browser, then paste it on the headless server using openclaw models auth paste-token --provider anthropic. This separation of token generation from token usage enables secure authentication without compromising on the benefits of headless deployment.
Memory issues manifest as gradual performance degradation or eventual crashes. The session.historyLimit configuration controls conversation history retention in memory. Setting this too high with active conversations consuming extensive context leads to memory exhaustion. Monitor memory usage during extended sessions and adjust the history limit accordingly. The recommended starting point is 100 messages, which balances context retention with memory consumption. For production deployments handling multiple concurrent users, lower limits per session prevent aggregate memory pressure.
Build and compilation errors affect users running OpenClaw from source rather than npm packages. The repository uses pnpm as its package manager, and attempting to use npm or yarn creates dependency resolution problems. After cloning the repository, run pnpm install followed by pnpm build. If the build fails, ensure you're on the main branch with latest changes using git pull origin main. The openclaw doctor command also validates build artifacts and can identify incomplete builds that cause runtime errors.
Automated Diagnostic Script
Manual troubleshooting works, but automation saves time and ensures consistency. The following script runs a comprehensive diagnostic sequence and outputs a shareable report. Save it as diagnose-openclaw.sh and run it whenever you encounter issues.
bash#!/bin/bash # Generates a comprehensive troubleshooting report echo "=================================" echo "OpenClaw Diagnostic Report" echo "Generated: $(date)" echo "=================================" echo "" echo "--- System Information ---" echo "OS: $(uname -s) $(uname -r)" echo "Node: $(node --version 2>/dev/null || echo 'Not found')" echo "npm: $(npm --version 2>/dev/null || echo 'Not found')" echo "OpenClaw: $(openclaw --version 2>/dev/null || echo 'Not found')" echo "" echo "--- OpenClaw Status ---" openclaw status 2>&1 || echo "Status command failed" echo "" echo "--- Gateway Status ---" openclaw gateway status 2>&1 || echo "Gateway status failed" echo "" echo "--- Model Status ---" openclaw models status 2>&1 || echo "Models status failed" echo "" echo "--- Doctor Report ---" openclaw doctor 2>&1 || echo "Doctor command failed" echo "" echo "--- Port Check ---" echo "Port 18789: $(lsof -i :18789 2>/dev/null | head -5 || echo 'No process or lsof unavailable')" echo "" echo "--- Recent Logs (last 20 lines) ---" tail -20 /tmp/openclaw/openclaw-$(date +%Y-%m-%d).log 2>/dev/null || echo "No log file found for today" echo "" echo "=================================" echo "Diagnostic complete. Share this output when seeking help." echo "Sensitive data has been automatically redacted." echo "================================="
This script collects system information, runs all diagnostic commands, checks port usage, and includes recent log entries. The output provides everything a support helper needs to understand your situation. OpenClaw automatically redacts sensitive information like API tokens from status output, making the report safe to share.
For Windows users running in WSL2, the same script works within the Linux environment. For native Windows PowerShell, equivalent commands exist but require different syntax. The cross-platform nature of Node.js means the OpenClaw CLI commands themselves work identically regardless of operating system.
Advanced users can extend this script with provider-specific health checks. Adding curl -s https://api.anthropic.com verifies basic connectivity to Anthropic's API endpoint. Similar checks for OpenAI and other providers help isolate network-level issues from authentication problems.
Prevention and Maintenance Guide
Preventing errors costs less effort than fixing them. A few regular maintenance habits keep OpenClaw running smoothly and catch potential issues before they cause failures. These practices apply equally to personal installations and production deployments.
Weekly health checks using openclaw status --deep verify that all configured providers remain accessible. Providers occasionally deprecate endpoints, rotate required credentials, or change authentication requirements. Weekly checks catch these changes before they cause production failures. Add this command to your calendar or automation workflow.
Keep OpenClaw updated to receive bug fixes and compatibility improvements. The development team actively addresses issues reported through GitHub, and updates frequently include fixes for provider-side changes. Run npm update -g openclaw@latest monthly, or more frequently if you're encountering issues that might be resolved in newer versions.
Monitor your API usage to avoid surprise rate limiting. Anthropic's Console shows current usage against your tier limits. Similarly, OpenAI and other providers offer usage dashboards. Understanding your consumption patterns helps you choose appropriate fallback strategies and tier upgrades.
Backup your configuration before making changes. Copy ~/.openclaw/ to a safe location before experimenting with new settings. If changes cause problems, restoring the backup returns you to a known-good state. This practice is especially valuable when trying solutions from online forums that might not match your specific setup.
Configure fallback models to maintain availability when primary providers experience issues. OpenClaw can automatically switch to alternative models when the primary choice fails. This redundancy prevents single-provider outages from blocking your workflow entirely.
Document your custom configuration choices. When you deviate from defaults, record why you made each change. Future troubleshooting becomes much easier when you understand the reasoning behind non-standard settings. This documentation proves invaluable when seeking help from others who assume default configurations.
Set up logging appropriately for your environment. Production deployments benefit from structured logging at the info level, while development and troubleshooting scenarios warrant debug level output. Configure logging in your openclaw.json with the logging.level and logging.file keys. The file log provides persistent records for post-mortem analysis, while console output helps with real-time debugging. Rotate log files periodically to prevent disk space exhaustion, especially on systems running OpenClaw continuously.
Consider implementing health check automation for production deployments. A simple cron job running openclaw health --json can pipe results to your monitoring system, alerting you to issues before users report them. The JSON output format makes parsing straightforward for any monitoring tool. Combine health checks with the diagnostic script from the previous section for comprehensive automated monitoring that catches both connectivity issues and configuration drift.
Test your disaster recovery procedures before you need them. Verify that your configuration backup can actually restore a working system by periodically testing the restore process on a separate machine or VM. Document the complete recovery procedure including any secrets or credentials stored outside the main configuration directory. This preparation transforms potential disasters into minor inconveniences with known recovery paths.
Frequently Asked Questions
How do I fix "openclaw: command not found" after installation?
The npm global bin directory isn't on your PATH. Add export PATH="$(npm prefix -g)/bin:$PATH" to your shell configuration file (~/.zshrc, ~/.bashrc, or ~/.bash_profile), then restart your terminal or run source ~/.zshrc. On Windows, ensure %AppData%\npm appears in your system PATH.
What does openclaw doctor --fix actually change?
The doctor fix command performs safe repairs including migrating deprecated configuration keys to current names, fixing file permissions on the .openclaw directory, creating missing required directories, and rewriting configuration files with corrected syntax. It doesn't delete data or reset authentication, making it safe to run whenever you suspect configuration issues.
Why does my session become unresponsive after switching models?
When switching models mid-session, the conversation history contains tool call IDs from the previous model that may not match the new model's expected format. Claude requires specific ID formats, and mismatches cause the session to hang. The fix is starting a new session with /new or the new session button. Unfortunately, this means losing conversation context during model switches.
How do I troubleshoot WhatsApp connection issues?
Run openclaw channels status --probe to test WhatsApp connectivity specifically. Common issues include device limits (unlink old sessions in WhatsApp mobile settings), corrupted auth state (delete ~/.openclaw/credentials/whatsapp/ and re-pair), and gateway not running. After any credential changes, restart the gateway with openclaw gateway restart.
What's the difference between openclaw status and openclaw doctor?
Status commands report current state without analysis, showing what's configured and running. Doctor analyzes configuration against the expected schema, identifying deviations and potential problems. Use status for "what's happening right now" questions and doctor for "is my configuration correct" questions.
Can I use OpenClaw without an Anthropic API key?
Yes, OpenClaw supports multiple AI providers including OpenAI, OpenRouter, Google, and others. Configure your preferred provider through openclaw models auth <provider>. You can also use multiple providers simultaneously, with automatic fallback between them. However, some features are Claude-specific and require Anthropic credentials.
How do I get help if these solutions don't work?
Share your diagnostic report (from openclaw status --all or the diagnostic script above) on GitHub Discussions or the Discord community. The report automatically redacts sensitive information. Include what you've already tried and your specific error messages. The community actively helps troubleshoot unusual configurations and edge cases. When posting to GitHub, use the bug report template if you believe you've found a software defect, or the discussion format for configuration questions and general help requests. The distinction helps maintainers triage effectively and ensures your question reaches people most likely to help.
Additional Resources
For ongoing troubleshooting support, several resources complement this guide. The official OpenClaw documentation provides authoritative information that stays current with each release. GitHub Issues (github.com/openclaw/openclaw/issues) contain detailed discussions of specific bugs, often including workarounds discovered by the community. The Discord community offers real-time help from both users and developers who can provide interactive troubleshooting assistance.
If you've successfully resolved an error not covered in this guide, consider contributing your solution. Open a pull request to the documentation repository, or post detailed steps in GitHub Discussions for others facing the same issue. The troubleshooting knowledge base grows through community contributions, and your unique configuration or use case might be exactly what someone else is struggling with.
For enterprise deployments or persistent issues that require dedicated support, professional assistance options exist through the OpenClaw ecosystem. API proxy services like laozhang.ai provide not just higher rate limits but also dedicated support channels for troubleshooting complex integration scenarios. When standard troubleshooting fails and you need guaranteed resolution timelines, professional support channels offer the accountability that community forums cannot.
